REVIEW
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
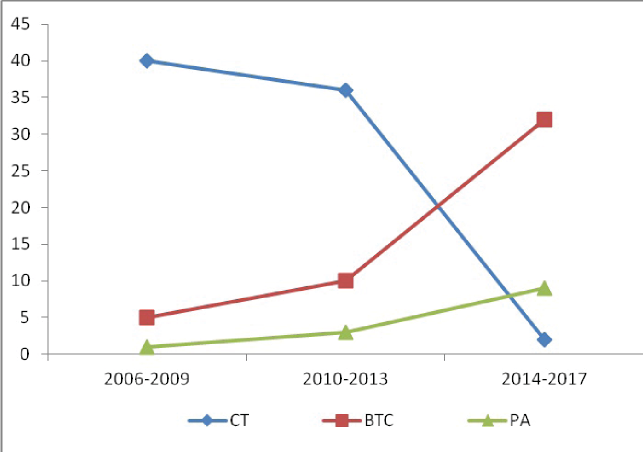
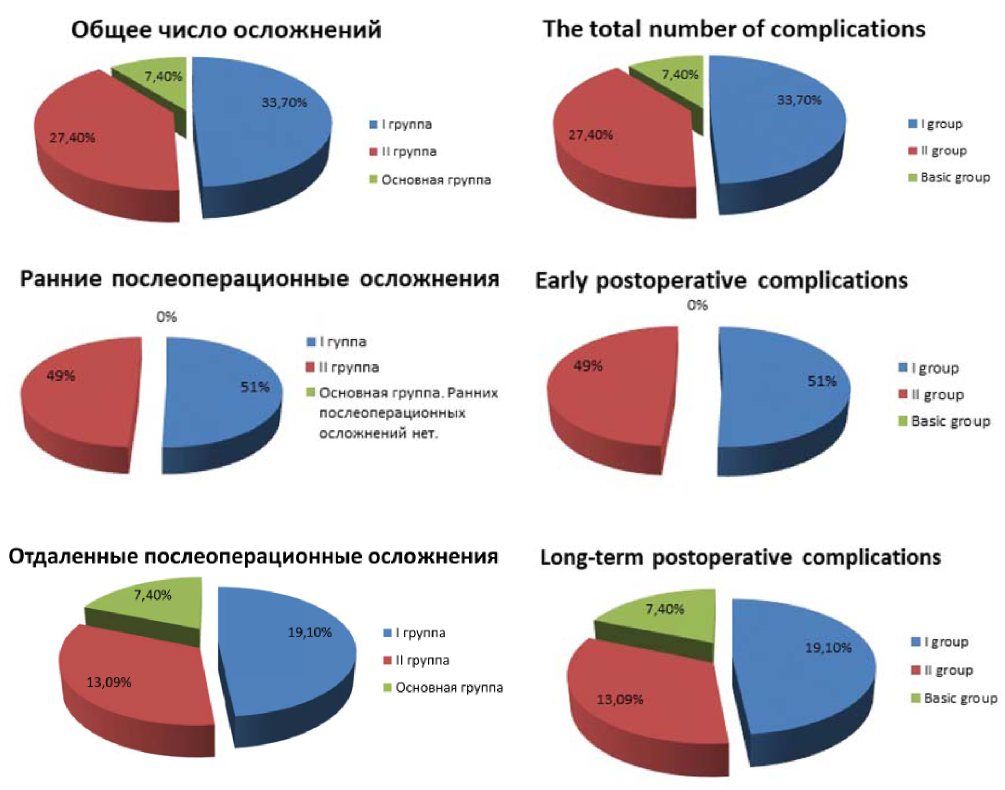
Objective: to assess the possibility of using mammary coronary bypass without bypass in high-risk patients and multifocal coronary artery disease, to analyze the immediate and long-term postoperative periods, to study clinical features in patient groups. Materials and methods: Th e study included 60 patients. All patients had a high risk of surgical intervention and a complicated pre-operative history. In the fi rst group, despite the multifocal lesion of the coronary arteries, for various reasons, we performed mammary coronary bypass on a working heart. In the second group, all patients underwent aorto-coronary bypass + mammary coronary bypass with bypass in a standard scheme using cold cardioplegia. Later, the results were evaluated aft er 30 days, 1 year, 5 years aft er the intervention. Results: It was showed that the immediate postoperative results and indices during the year had a positive dynamics - the class of angina pectoris decreased, the hemodynamic parameters changed. In addition, the rejection of bypass in patients with a complicated anamnesis made it possible to exclude complications from the excretory and nervous systems that we observed in the second group. In the future, we observed an increase in the class of angina in the fi rst group. Th e recurrence of angina pectoris is associated, in our opinion, with the progression of coronary atherosclerosis, an increase in existing stenoses and the appearance of new stenoses. Conclusions: mammary coronary bypass without bypass can be successfully used in high-risk patients and multifocal lesion of the coronary bed. Th is can be regarded as an outcome with extremely dangerous use of bypass for complete myocardial revascularization. Th e immediate results are positive and minimize postoperative risk from adjacent organs and systems. Anatomical and functional state of mammary coronary bypass is satisfactory, both in the near and the delayed period. Long-term observations indicate an increase in the class of angina and complications of IHD in this group of patients. Th e way out in this situation we see in the combined work of the surgical and endovascular team.
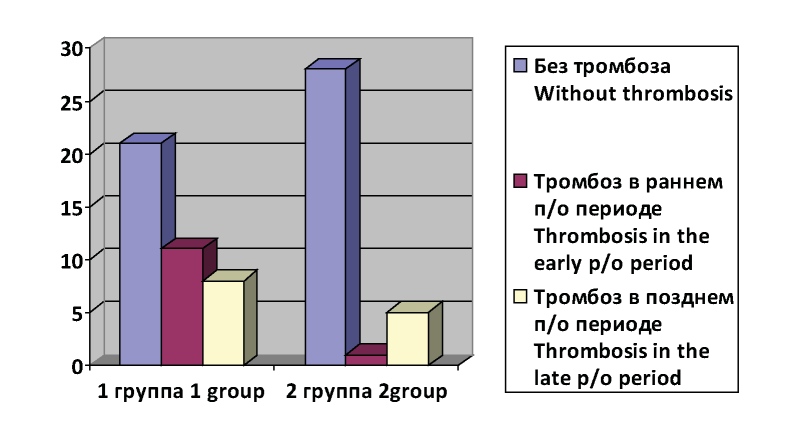
Objective: to improve the results of treatment of patients with obliterating atherosclerosis with critical ischemia of the lower extremities by individual selection of anticoagulant therapy for the prevention of thrombosis aft er reconstructive surgery on the arteries of the lower extremities. Materials and methods: 82 patients were divided into 2 groups: 1 group (48 patients) - reconstructive surgery on the arteries of the lower extremities and anticoagulant therapy under the control of the coagulogram. 2 group (34 patients) - reconstructive operations with the selection of anticoagulant therapy with the help of hemostasiogram indicators and the T-2 thrombodynamics test. Results: Out of 48 patients in the 1 study group, a good eff ect was observed in 36 patients (75.00%), in 9 (18.75%) - satisfactory, and in 3 cases (6.25%) - unsatisfactory. In the 2nd group: good results - 33 (97.06%) patients, and in 1 (2.94%) patients - satisfactory. Unsatisfactory results were not. Th e number of repeated operations within 1 year, performed in the 1st group, was statistically signifi cantly 2 times greater than in the second group. All the second operations are associated with the development of thrombotic complications. With a combination of the majority of hemostasiogram and «Trombodynamics T-2» tests, the dose of heparin therapy was adjusted, increasing by 2500 units, i.е. the patient received 7500ED 4 p / day. If during the «T-2 thrombodynamics» and coagulogram on the 6th day aft er surgery, hypercoagulation was determined, then the dose of heparin increased again by 2500 units. Conclusions: Comparative analysis of hemostasiogram indices in the fi rst hours aft er the performed operative treatment is not very useful for predicting the frequency of thrombotic complications, while 6 days aft er operative treatment it indicates the presence of statistically signifi cant diff erences between the two study groups. Th at indicates a more adequate selection of a dose of heparin in the second group.
Objective: to study pro- and anti-infl ammatory cytokines serum levels at postmenopausal osteoporosis and their changes depending on separate polymorphic options of VDR, COL1A1 and LRP5 genes. Materials and methods: 180 postmenopausal women (60,0±0,77 years) were examined. Th e osteodensitometry was carried out by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry method. Detection of 283 A>G (BsmI, rs1544410) polymorphisms of VDR gene, -1997 C>A (rs1107946) and 1546 (6252) G>T (Sp1 S>s, rs1800012) of COL1A1 gene, 3989 C>T (Ala1330Val, rs3736228) and 1999 G>A (Val667Met, rs4988321) of LRP5 gene was carried out by real-time PCR method. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used for defi nition of serum levels of interleukin (IL) -1β, -4, -6, -8, -10, -17A, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interferon gamma (INF-γ), osteoprotegerin (OPG), receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL). Results: it was established that women with postmenopausal osteoporosis had (P<0,05) increased serum IL-1-β, IL-8, IL-17A, TNF-α, RANKL concentration and decreased IL-4, IL-10 levels. Patients with GG genotype of rs1544410 polymorphism had also increased (P<0,05) IL-1-β, RANKL levels, OPG/RANKL index and decreased IL-10 values. Women with GT or TT genotypes of rs1800012 polymorphism of COL1A1 gene had (P<0,05) decreased IL-10, OPG values, OPG/RANKL index, but persons with CA or AA genotypes of rs1107946 polymorphism of COL1A1 gene had increased IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, RANKL levels. IL-10 concentration decrease (P<0,05) was established for patients with GA genotype of rs4988321 polymorphism and CT or TT genotypes of rs3736228 polymorphism of LRP5 gene. Conclusion: the obtained data refl ect important pathogenetic aspects of postmenopausal osteoporosis and can be used for development of individualized treatment-and-prophylactic actions for women.
Objective: Evaluation of the eff ectiveness and identifi cation of the benefi ts of a video-assisted fi stula treatment method using
fi stuloscopy, in comparison with traditional methods of surgical treatment of complex forms of chronic paraproctitis, trans- and extrasphincteric, relapsing rectal fi stulas. Materials and methods: A complex analysis of the results of surgical treatment was carried out in 228 patients with chronic paraproctitis, transphincteric, ectrasphincteric, including recurrent rectal fi stulas, divided into three groups (main and two control), depending on the surgical methods of chronic paraproctitis used. Results: the result of surgical treatment of pararectal fi stulas in the three study groups was compared. Th e eff ectiveness of treatment was assessed by the results of immediate and long-term postoperative period. It has been established that the use of a video-assisted fi stula treatment method using fi stuloscopy excludes the presence of an extensive postoperative wound in the perianal region, which signifi cantly reduces the likelihood of its secondary infection, and the sphincter trauma, and in fact virtually eliminates its insuffi ciency. Th e use of video-assisted method of treatment of fi stulas made it possible to reduce the number of postoperative complications. Conclusions. Th e fi nal results (92.7% of favorable outcomes) allow us to recommend a video-assisted treatment for fi stulas for wide practical implementation.
EXPERIENCE EXCHANGE
Objective: To evaluate the effi cacy and safety of a combination of direct antiviral drugs - paritrapeprivir, ritonavir, ombitasvir and dasabuvir in patients with compensated cirrhosis of HCV-etiology. Materials and methods: A prospective cohort study involved 30 patients with compensated cirrhosis of the liver with HCV etiology (class A in Child-Pugh) caused by the 1b genotype of the virus. All patients received a formal combination of direct antiviral drugs - paritrapeprivir, ritonavir, ombitasvir and dasabuvir (PROD) for 12 weeks. Effi cacy evaluation was conducted to achieve a sustained virologic response 24 weeks aft er the end of antiviral treatment (VDU 24). Results: Two weeks aft er the start of treatment the virus stopped being detected in 21 people (70%), aft er 4 weeks - in all patients. VDU 24 was also achieved in 100% of cases. One patient, operated prior to the initiation of antiviral treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), relapsed both HCC and HCV infection 36 weeks aft er the end of the antiviral treatment. Adverse events in the form of mild headache and nausea were noted only in two patients (6.7%) and had an unexpressed and short duration. Conclusions: in real clinical practice, high effi cacy of direct antiviral drugs - PROD in patients with compensated cirrhosis of HCV-etiology (in 96.7% of patients) was demonstrated at a relatively low incidence (6.7%) of side eff ects.
CASE REPORT
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)