OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
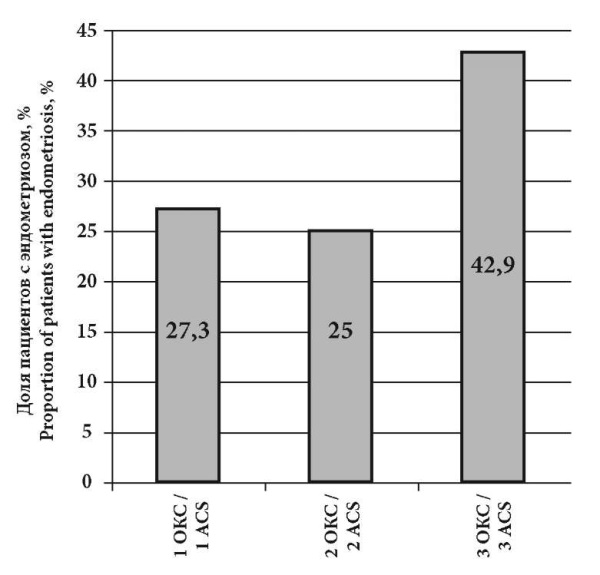
Objective: to analyze cases of surgical correction of uterine scar failure aſter cesarean section, to determine the frequency of detection of endometriosis of the uterine scar according to histological findings and to identify the effectiveness of diagnostic methods.
Materials and methods: a retrospective analysis of the medical records of 52 patients from January 2022 to December 2024, who underwent surgical correction of a uterine scar aſter cesarean section with its failure, was carried out.
Results: our correlation analysis revealed that in most cases, uterine scar endometriosis was asymptomatic, however, in rare cases, a connection was observed between patients’ complaints of abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) and uterine scar endometriosis. The absence of complaints in endometriosis confirms its asymptomatic course. Due to the latent and difficult to diagnose course of the disease, as part of pre-pregnancy preparation in women with a uterine scar, it is necessary to use a comprehensive diagnostic approach, combining non-invasive methods with hysteroscopy, to increase the frequency of detection of scar endometriosis. This will allow timely surgical treatment and prevent disease progression.
Conclusion: ultrasound examination as a method for diagnosing endometriosis of the uterine scar aſter ACS showed low sensitivity in detecting this pathology, despite the high resolution of modern ultrasound devices. Magnetic resonance imaging and diagnostic hysteroscopy are recommended as diagnostic methods. In turn, a combination of methods for diagnosing a scar on the uterus aſter ACS as part of pregravid preparation will make it possible to increase the frequency of detecting endometriosis of the uterine scar and will allow timely surgical treatment of the identified pathology.
Objective: to evaluate the results of using the autograſt of the tendon of the semitendinosus muscle in the treatment of apical prolapse in postmenopausal patients.
Materials and methods: the study included 3 postmenopausal women with POPQ grade 2–3 apical prolapse. This group underwent surgical treatment in the following scope: laparoscopic supravaginal amputation of the uterus with appendages, promontofixation of the cervical stump using autograſt of the tendon of the semitendinosus muscle. The outcome of pelvic prolapse correction was evaluated in the early and late postoperative period, as was the assessment of knee joint functionality.
Results: the outcome of surgical treatment of apical prolapse in postmenopausal women with the use of the autograſt of the tendon of the semitendinous muscle is comparable to the results of surgical techniques with the use of the mesh implant in terms of time and efficiency, but the described technique allows to avoid mesh-associated complications. There were no complications during and aſter the surgery, decrease in the functional activity of the knee joint, or postoperative recurrences during the follow-up period.
Conclusions: non-standard approach, relative simplicity, preliminary results of the applied operative technique justify the introduction of autotransplantation in pelvic prolapse surgery. It is necessary to continue the study with a larger group of patients to evaluate the long-term results of the surgical procedure.
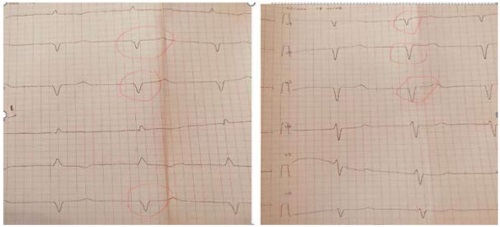
The terms radiologic isolated syndrome (RIS) and clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) are currently used in practical healthcare. RIS are foci in the white matter of the brain detected on MRI, which are oſten interpreted as a demyelinating process and suggest the presence of multiple sclerosis (MS) in patients. These changes do not have clinical manifestations and neurologic symptoms characteristic of MS. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic progressive disease of the central nervous system. MS is widespread among women of reproductive age, which poses a challenge to both obstetricians and neurologists in terms of addressing the planning and management of pregnancy and childbirth. Therefore, the clinical and prognostic significance of these changes in patients with RIS remains controversial. But it is undeniable that patients with RIS are at high risk of developing MS: about 2/3 of patients have progression according to MRI and about 1/3 of patients have clinical symptoms within 5 years of follow-up. In the case that we would like to present to you, a separate clinical episode developed against the background of RIS, manifested by a seizure syndrome in the postpartum (aſter cesarean section) period, which suggested that this was the debut of CIP against the background of an existing but undetected RIS. This prompted us to describe this case and present it to researchers and practicing physicians.
Objective: to study the frequency and structure of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos obtained as part of ART in Kuzbass women with infertility.
Material and methods: 58 embryos obtained as a result of in vitro fertilization-intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF-ICSI) were examined for the presence of aneuploidies at the Center for Family Health and Reproduction «Krasnaya Gorka» by performing (preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy) PGT-A.
Results: 60.3% (35) of the embryos contained chromosomal abnormalities. Of these, 77.08% of embryos had aneuploidy, 18.75% had mosaicism, and 4.17% had polyploidy. In the cohort of women whose AMH levels were reduced, 62.5% of embryos had CA. The frequency of CA embryos in women over 35 years of age is 57.1%. Analysis of the CA structure of embryos in a cohort of patients with pathospermia revealed that 57.7% of embryos were euploid. 42.31% of embryos had CA in their genetic profile.
Conclusions: comparing the detected frequency of chromosomal abnormalities (CA) in embryos with the results of studies by foreign colleagues, we can say that the level of euploid, aneuploid and mosaic embryos obtained aſter PGT-A is approximately equal in different populations: 60% of embryos have CA. Among all CA, aneuploidies dominate with a frequency of 77.08%. Among aneuploidies, trisomy of chromosome 16 was prevailed (12.5%). The incidence of mosaicism was 18.75%.
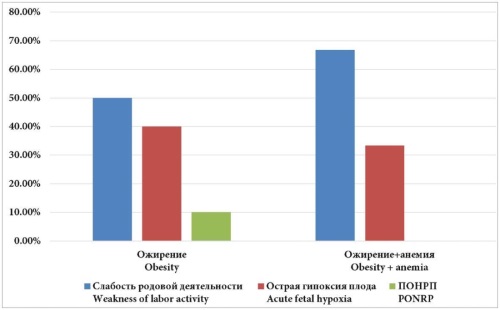
Objective: to evaluate the effectiveness of programmed birth in women with obesity and anemia.
Materials and methods: a prospective cohort study was conducted at the clinical site of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology with a course in perinatology of the Medical Institute of Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia in the maternity hospital at the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution City Clinical Hospital No. 29 named aſter N.E. Bauman of the Moscow Health Department. The study included 238 pregnant women with obesity and anemia, who were stratified into 4 groups depending on the degree of obesity (I, II and III) and group IV, which included a combination of obesity and anemia. All respondents included in the study were assessed for obstetric and perinatal outcomes of childbirth depending on the method of delivery: spontaneous labor, PR and abdominal delivery.
Results: programmed labor was associated with fewer complications during childbirth and the postpartum period. Statistical analysis showed: 1) programmed delivery reduces the frequency of cesarean section in women with obesity and anemia; 2) programmed delivery in women with obesity and anemia, compared to spontaneous delivery, reduces the duration of the first stage of labor; 3) programmed delivery reduces the frequency of postpartum complications: compared to spontaneous delivery — hypotonic bleeding, ruptures of the birth canal; compared to cesarean section — reduces the frequency of uterine subinvolution.
Conclusions programmed delivery reduces the frequency of abdominal delivery and postpartum complications in patients with obesity and anemia.
PSYCHIATRY
The article highlights the problem of the prevalence of anxiety disorders in modern conditions, as well as the role and place of agoraphobia in the structure of non-psychotic mental disorders. Our own data on a sample of patients with agoraphobia are presented. It was found that agoraphobia was most oſten found in the context of anxiety disorders and social phobias (“F40-41”). In the clinical case, the mechanism of agoraphobia formation is shown when panic attacks appear in the clinical picture. It is indicated that in order to solve therapeutic problems, it is necessary to choose an integrated approach in treatment: a combination of drug and psychotherapeutic effects. A long-term catamnesis has demonstrated that the therapy performed has led to the patient’s recovery and increased his adaptive capabilities.
The literature review is dedicated to the problem of mentism a well-known yet ambiguous phenomenon of impaired spontaneity of thought. The presented literary material is based on a search for Russian and English articles in the following databases: ELibrary.ru, Web of Science, Scopus, Clinical Case, PubMed, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. The search for articles was conducted using the keywords: mentism; spontaneity of thought; automatism; basis symptoms of schizophrenia. Inclusion criteria: full-text articles in Russian and English; original research; Cochrane reviews; clinical observations; publication date from 1895 to 2025. Exclusion criteria: abstracts, theses, educational materials; publication date before 1895. A total of 126 publications were found. 28 publications met the inclusion/exclusion criteria. This review provides detailed descriptions of the phenomenon of mentism across different historical periods. A possible typology of mentism is proposed, the relationship of mentism with affective pathology and schizophrenia is examined, the position of mentism in contemporary diagnostic classifications, and its interpretation as a basis symptom of schizophrenia and a symptom of affective disorders is discussed. The authors of the review present a list of unresolved questions related to mentism, suggesting that clarifying these issues could be beneficial for improving the quality of diagnosis and therapy for mental disorders.
INTERNAL DISEASES
Objective: to evaluate the quality of life of patients with chronic pancreatitis and erosive and ulcerative changes of the stomach and duodenum before and aſter therapy.
Materials and methods: a survey of 40 patients with chronic pancreatitis and 50 patients with erosive and ulcerative changes of the stomach and duodenum using the SF-36 questionnaire; processing of the obtained results using a computer program.
Results: indicators of physical and mental health in patients with chronic pancreatitis were significantly lower at admission.
Conclusions: the use of the SF-36 questionnaire in the practice of a gastroenterologist will help identify and correct psychological problems in order to increase the effectiveness of therapy for diseases of the digestive system.
ENDOCRYNOLOGY
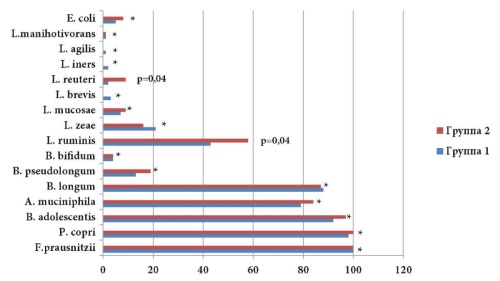
Objective: to study the features of the content of some types of microorganisms in the colon in obese patients and healthy individuals with normal body weight using metagenomic sequencing. Materials and methods: a total of 265 people (44 men and 221 women, average age 47.1±4.8 years) were examined. Two clinical groups were formed: healthy individuals with normal body weight (n=129) and obese patients (n=136). The composition of the intestinal microbiome was assessed using metagenomic analysis. DNA was isolated from fecal samples and sequencing of the v3-v4 variable region of the 16S rRNA gene was performed. Results: statistically significant (p<0.05) differences in the quantitative and qualitative parameters of some types of microorganisms in the colon of healthy individuals without obesity and in obese patients were revealed. The number of P. copri was increased in obese patients. and decreased F. prausnitzii, B. adolescentis and B. longum. Conclusions: the obtained results demonstrated certain species differences in the intestinal microbiome in healthy individuals and in obese patients.
CARDIOLOGY
A clinical case of amyloid cardiomyopathy associated with multiple myeloma with the development of chronic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction refractory to therapy is presented. The role of clinical signs, especially “red flags” of amyloidosis, is studied, as well as the need to increase physicians’ awareness of the symptoms and signs of amyloid cardiomyopathy, and early detection and treatment of the pathology. Current diagnostic methods are discussed, including histological examination and immunophenotyping, which can improve the patient’s prognosis.
Objective: to evaluate the prevalence of congenital and acquired thrombophilia in patients with myocardial infarction (MI).
Materials and methods: thrombophilic factors were studied in patients included in the registry of acute coronary syndrome in the Krasnodar Territory. The sample included patients who were admitted for acute myocardial infarction at the Ochapovsky Regional Clinical Hospital, from November 2023 to November 2024, and who meet the universal diagnostic criteria for acute myocardial infarction. Based on the coronary angiography data, two groups were identified: 1 — patients with coronary artery stenosis 150%), lipoprotein (a) (> 30 mg/dl) and homocysteine (≥15 µm) were evaluated.
Results: a comparison was conducted of 100 sequentially enrolled patients with myocardial infarction without obstructive (stenosis 50%) coronary arteries (MIOCA) (the average age is 50.8±12.9 years). The most significant incidence of hereditary thrombophilia was found in the group of patients with MINOCA (21 patients (21%) versus 9 (8.8%) with MIOKA (p=0.0076). In addition, hyperhomocysteinemia, APS, and elevated factor VIII were also more common among MINOCA patients. APS was detected in 13 (13.0%) patients with IBD, mainly in a single-positive form, and prevailed in patients with non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (11 patients (11.0%) versus 2 patients (2.0%) with ST segment elevation, p=0.0035). In turn, lipoprotein (a) was more common in patients with MIOKA (32 patients (31.4%) versus 18 patients (18.0%) with MIOKA, p=0.0221.
Conclusions: the prevalence of thrombophilia, including APS, is higher in the group of patients without significant coronary artery damage. The study demonstrates that screening and detection of thrombophilia in patients with MINOCA is of high clinical importance. Based on the data obtained, it can be assumed that the appointment of long-term anticoagulant therapy will have a favorable prognosis in patients with IBD with certain disorders, especially with AFS.
PAEDIATRICS
This article presents a clinical case of a patient with congenital hyperinsulinism. The girl, born on in a state of moderate severity due to symptoms of respiratory failure, neurological symptoms, on the 1st day of her life was transferred to department of pathology of newborn and premature infants from the maternity hospital of the city clinical hospital. During the observation period, persistent hypoglycemia was noted in the department, which was corrected by intravenous infusion of 10% glucose, when attempting to cancel intravenous drip administration of 10% glucose, episodes of hypoglycemia (up to 1.8mmol/l) resume. Taking into account the increase in blood insulin levels to 67.2 mg/l, the patient was transferred to the Scientific Research Institute of Obstetrics and Pediatrics (NIIAP) for further examination and choice of treatment tactics. During hospitalization at the NIIAP, the diagnosis was established: Congenital hyperinsulinism — against the background of hypoglycemia, 1.2 mmol /l insulin level — 10 µmed /ml. From 01.07.2024, with the consent of the mother, according to vital indications, Diazoxide (Proclicum) therapy at a dose of 20 mg / day (5.0 mg / kg/ day) was started in the department under the control of glycemia, against the background of which there was a tendency to stabilize glycemic indices, fluctuations in the level of glycemia according to the glucose meter from 2.7 mmol / l to 5.0 mmol / l, from 08.07.24 the abolition of infusion therapy of 10% glucose. The therapy is tolerated satisfactorily; no significant side effects were found. However, given the persistent hypoglycemia of 2.7 mmol / l against the background of the fasting interval, the dose of Diazoxide was increased to 25 mg / day (5.5 mg / kg / day). The child continues to be in the hospital.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
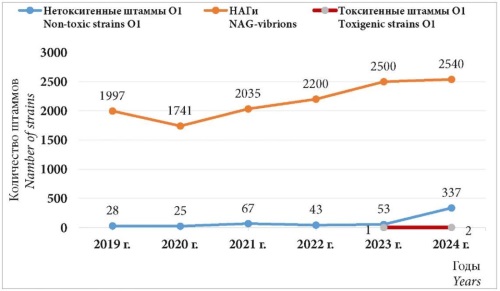
Objective: to analyse the possibility of Vibrio cholerae survival in surface reservoirs of the Russian Federation subjects under conditions of low water temperature, compared to the temperature optimum for the growth and reproduction of these microorganisms in environmental objects (EO).
Materials and methods: official data of the reference centre for cholera monitoring on the detection of Vibrio cholerae strains in the aquatic environmental objects of the Russian Federation subjects within the framework of monitoring studies for the period from 2019 to 2024 were used. Monitoring studies were organised and conducted in accordance with the current regulatory and methodological documentation. All isolated Vibrio cholerae strains were identified by regulated bacteriological, serological, molecular-biological methods.
Results: 553 strains of Vibrio cholerae O1 serogroup (three of them toxigenic) and 13013 strains of NAG-vibrios were isolated for the period from 2019 to 2024. The range of minimum water temperatures of surface reservoirs from which the first strains of Vibrio cholerae were isolated in the administrative territories of types I–III on cholera epidemic manifestations was in the range from 1 °C to 15 °C, which is lower than the temperature optimum (above +16 °C) for their growth, and indicates the possibility of survival of these microorganisms in conditions of low temperatures of water bodies, and, therefore, does not exclude the possibility of spreading infection by water in the event of a toxigenic strain entering the reservoir.
Conclusions: detection of NAG vibrios and non-toxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae O1 serogroup in the water of surface reservoirs at temperatures up to 15 °C is an indicative sign of the existence of conditions conducive to the spread of infection in case of cholera importation into the territory of the Russian Federation and indicates the expediency of an earlier start and a later end of cholera monitoring studies in Russia.
Objective: analysis of current literature on work-related diseases in health care workers (HCW).
Matherials and methods: the literature review was performed using RSCI, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science (Core Collection) databases on 13 February 2025 for the following keywords: healthcare workers, work-related diseases, occupational diseases, health preservation, health of healthcare workers. Articles published between 2005 and 2024 were selected for analysis.
Results: HCW are characterized by high occupational morbidity compared to other socio-professional groups and the general population due to exposure to various harmful factors in the workplace. Among HCW, chronic work-related diseases prevail, which include diseases of the circulatory system, metabolic syndrome, overweight and obesity, diabetes mellitus, mental disorders, diseases of the musculoskeletal and reproductive systems, digestive and respiratory organs, as well as allergic and infectious diseases.
Conclusions: regulatory legal documents regulate the issues of control and prevention of the negative impact of harmful and dangerous factors on the HCW. Active implementation and modernization of existing health-saving measures is required due to the high risk of work-related diseases among HCW.
OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE
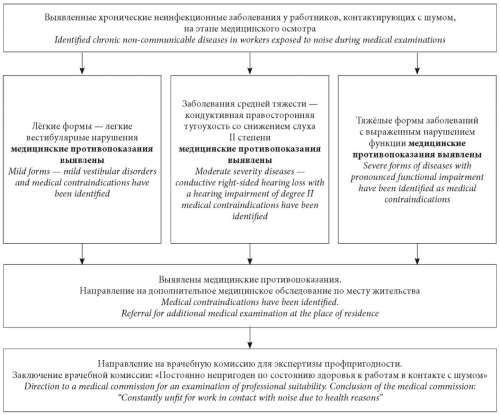
A comprehensive search was conducted for literary sources devoted to the problem of assessing the professional suitability of workers in contact with industrial vibration and noise in the international database PubMed (Medline) and the scientific electronic library Library. The search was conducted by keywords: professional aptitude examination, medical examinations of employees, general and local vibration, industrial noise. The selection criteria were full-text articles published over the past 25 years, 48 of these articles were published in the last 10 years. Of the 91 sources found, 46 papers that met the selection criteria and 1 article published in 1999 (which is fundamental and reveals the features of the pathogenesis of vibration disease) were used to conduct this analytical review. Based on the analysis of literature data and regulatory documents, information is provided on the domestic experience in determining the professional suitability of employees. Information is given on the main stages of the formation and improvement of the system for determining the professional suitability of workers with physical factors. Modern approaches to rationing and special assessment of the working conditions of workers in contact with vibration and noise are described. The issues of assessing medical contraindications for performing work with vibration and noise in the process of mandatory medical examination and professional aptitude examination in the conditions of a medical commission are considered. An algorithm for assessing the professional aptitude of workers in contact with vibration and noise is proposed.
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)