3.1.4. OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Objective: this article is a scientific review of the literature devoted to the important problem of ovarian endometrioma recurrence in the postoperative period. The data were analyzed based on foreign and domestic sources e-Library, Springer Nature, Wiley Journals, PubMed for 2016–2023 using the following keywords: «endometrioma», «risk factors», «recurrence», «prediction», «biomarkers». In the process of literature review, a significant relationship between infertility and ovarian endometriosis has been established, but all mechanisms in the occurrence of infertility in ovarian endometriomas remain incompletely understood. Noninvasive markers involved in the pathogenesis of the disease - apoptosis, angiogenesis, adhesion, as well as the possibilities of the diagnostic model of noninvasive diagnosis of endometriomas in the postoperative period are described in detail. The data on the effectiveness of drug therapy, as a way of preventing postoperative recurrence of the disease are highlighted and summarized.
PSYCHIATRY AND NARCOLOGY
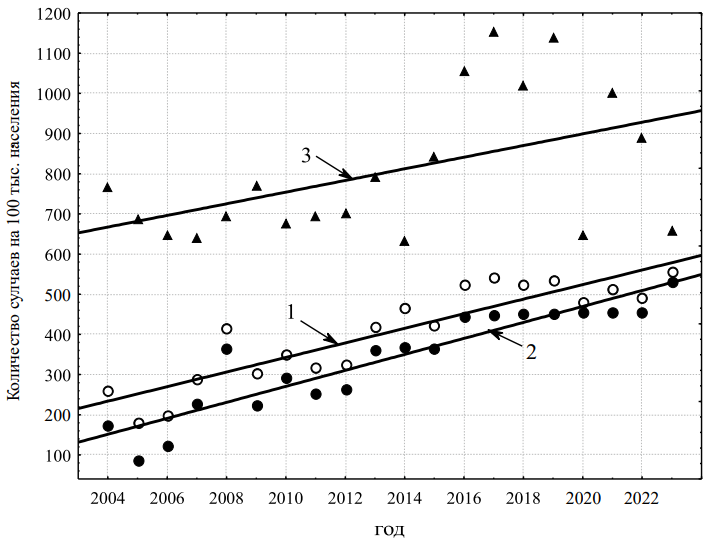
Objective: performing a comparative analysis of various indicators of mental and behavioral disorders in the population living in the Lugansk region over a long period of time, followed by the development of scientifically based recommendations. Materials and methods: the research was carried out in the Luhansk region for the period 2004–2023. The total time interval of 20 years is divided into two equal ten-year periods: peacetime (2004–2013) and wartime (2014–2023). The work used official data from the annual reports of the statistical department of the Luhansk Clinical Neuropsychiatric Hospital of the LPR and data from the Lugansk Coordination Center for Health Protection “Indicators of public health and activities of medical organizations of the Luhansk region”, “Indicators of public health and activities of medical organizations of the Luhansk People’s Republic” for 2004–2023. Results: when comparing the peacetime and wartime periods, a statistically significant deterioration in all indicators characterizing mental health during wartime was proved. Conclusions: the depressive wartime environment in the Luhansk People’s Republic is a significant risk factor for the occurrence or exacerbation of mental disorders, an increase in the duration of inpatient treatment of patients with mental and behavioral disorders, a deterioration in the clinical prognosis of the disease and, as a result, disability
Objective: to analyze the main methods for determining the likelihood of the risk of recidivism among minors within the framework of an inpatient comprehensive forensic psychiatric examination in criminal proceedings. Materials and methods: to study the characteristics of the mental state of minors undergoing an inpatient forensic psychiatric examination in criminal cases from 2019 to 2023 at a state expert institution, a retrospective study of 42 expert reports was conducted. Results: using methods for determining the likelihood of the risk of repeated unlawful acts, a very high degree of risk of recidivism of offenses was identified in 22% of the experts in the specified age group and, at the same time, it does not correlate with expert decisions on sanity/insanity and recommended compulsory medical measures aimed at the experts. Conclusion: in the context of offenses committed by minors, assessing the likelihood of recidivism is a key factor determining the future fate of a teenager and his rehabilitation strategy. Forensic psychiatric examination in this case becomes not just a formal procedural stage, but a tool for in-depth analysis of personality and identification of the causes of deviant behavior, allows us to identify the most significant causes of social maladaptation of adolescents, determine the degree of criminal responsibility, and also plays an important role in the development of individual rehabilitation programs and resocialization, which will affect the effectiveness of crime prevention among adolescents and ensuring their rehabilitation.
3.1.18. INTERNAL DISEASES
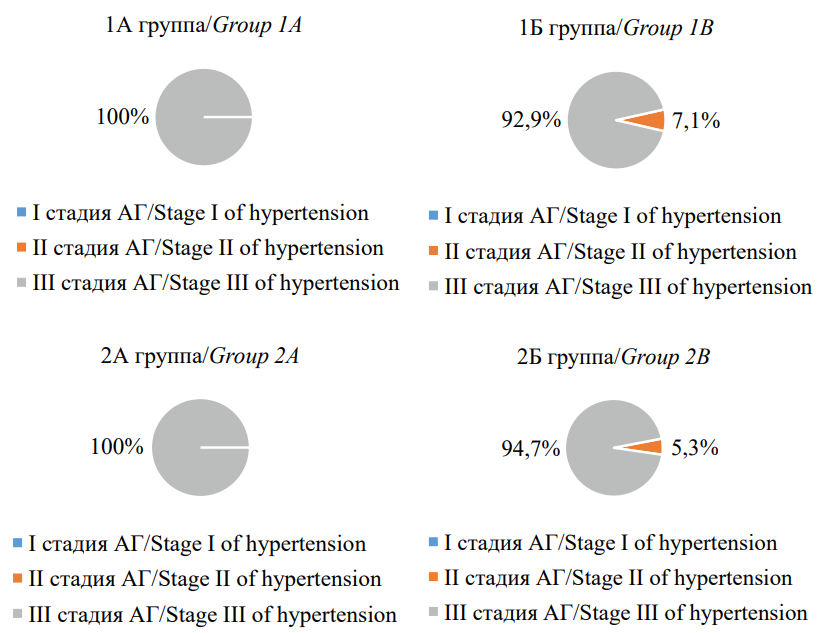
Objective: to evaluate the parameters of central aortic pressure in patients with arterial hypertension (AH) depending on the presence of chronic heart failure (CHF) and senile asthenia syndrome (SSA). Materials and methods: 320 patients with AH were divided into four groups: group 1A — patients with AH, SSA and CHF (n=84), group 1B — patients with AH, SSA without CHF (n=84), group 2A — patients with AH, CHF without SSA (n=77), group 2B — patients with AH without CHF and without SSA (n=75). Central aortic pressure parameters were determined using a BPLab ABPM device using Vasotens technology (“Petr Telegin”, Nizhny Novgorod). To process the obtained data, statistical programs STATISTICA 12.0, SPSS 21.0, MedCalc 9.3.5.0 were used. Results: in patients with AH, CHF and SSA, higher average daily values of SBP ao were recorded compared to both patients with AH and CHF without SSA (p=0.004) and with AH, SSA without CHF (p=0.019). The presence of SSA led to higher AIx ao values both in patients with hypertension, SSA and CHF (p<0.001), and in patients with AH and SSA without CHF (p<0.001). In patients with AH and CHF, regardless of the presence of SSA, higher rates of PBP ao (p<0.001), AIx ao (p<0.001), ED (p<0.001) and lower rates of SERV (p<0.001) were recorded. When assessing the degree of influence of CHF or SSA, it was shown that CHF had a more pronounced effect on PBP ao (p<0.001), ED (p<0.001) and SERV (p<0.001) indicators than SSA. Conclusion: in patients with AH aged 80 years and older, the development of both SSA and, to a greater extent, the presence of CHF was accompanied by an increase in central aortic pressure. With a combination of AH, CHF and SSA, the most pronounced disturbances in the elastic properties of blood vessels were observed, which is associated with a high cardiovascular risk.
3.1.19. ENDOCRINOLOGY
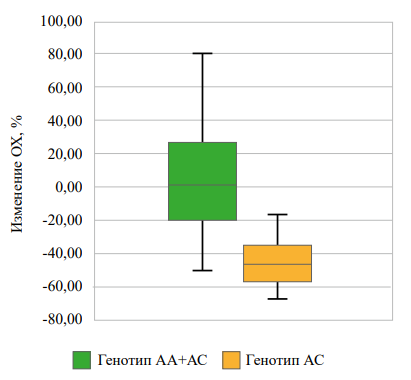
Objective: to analyze the association of rs622342 SLC22A1 with the short-term changes in fat and carbohydrate metabolism parameters in various types of early carbohydrate metabolism disorders therapy. Materials and methods: the results of management of 89 patients with excess body weight and risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus development were analyzed. For 3 months, 53 patients followed diet therapy, 36 patients took metformin in addition to the diet. All of the patients were genotyped for rs622342 SLC22A1. Also initially and 3 months after the beginning of therapy fasting plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, low-density and high-density lipoproteins, tryglicerides were measured. Statistical processing was carried out using parametric and non-parametric criteria. Results: 3 months after the start of diet therapy, homozygous СС-carriers of the rs622342 SLC22A1 showed a significant decrease in total cholesterol and triglycerides compared with A-allele carriers. These changes were not observed when metformin was added to diet therapy. There were no significant differences in changes of fasting plasma glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels in groups with different management. Conclusions: carriers of CC rs622342 SLC22A1 are characterized with the significant decrease in total cholesterol and triglycerides levels compared to the A-allele carriers after 3 months of standard diet therapy; when metformin is added to the treatment regimen, these changes are not observed.
CARDIOLOGY
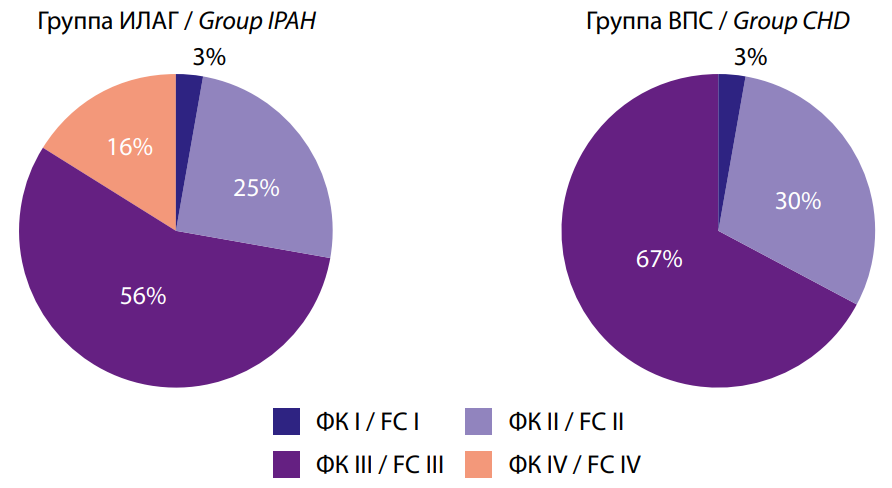
Objective: to study the clinical and pathogenetic features of idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in congenital heart defects, based on a 10-year follow-up of patients in the Rostov region. Materials and methods: the analysis included patients over the age of 18 who are registered in the Rostov region with various etiologies of PAH, including with IPAH and PAH-CHD. Two groups of patients were identified: 1st – patients with IPAH (n=32) and 2nd – with PAH in congenital septal heart defects (defects of the atrial or interventricular septa) (n=30). All patients underwent electrocardiography, echocardiography, and condition assessment using the clinical condition assessment scale, as well as the effectiveness of a screening questionnaire for early diagnosis of PAH. Results: it was found that patients with IPAH are older, seek medical help more often, have more pronounced clinical symptoms compared to patients in the 2nd group, and require more aggressive treatment. Patients with PAH in congenital heart defects are less likely to seek help, and have a longer period from the onset of the first symptoms to the detection of pulmonary hypertension. Patients in group 1 required increased PAH-specific therapy in 53% of cases, and patients in group 2 – in 19% (p<0.05). Conclusions: clinical and pathogenetic features of idiopathic PAH and against PAH in congenital heart defects have been identified, which makes it possible to optimize the early diagnosis and treatment of such patients
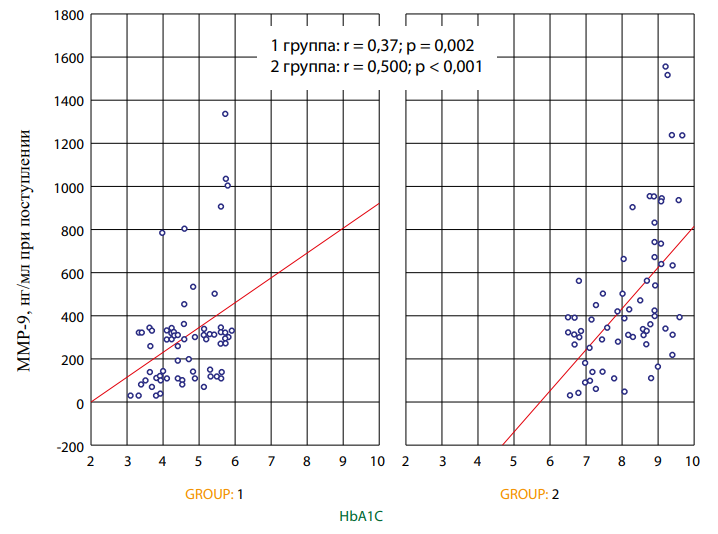
Objective: to study the pulse wave propagation rate and the level of matrix metalloproteinase type 9 in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention in the presence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Materials and methods: the study included 136 patients of both sexes. The first group consisted of 69 patients with STEMI+AH, the second group included 67 patients with acute STEMI+AH+DM2. The patients underwent analysis of the level of matrix metalloproteinase type 9, analysis of pulse wave propagation velocity, Statistical processing of the study results was carried out using Excel spreadsheets and the Statistica 10 statistical software package (StatSoftInc.). Results: at the stationary stage, the level of MMP-9 in the first group ranged from 28 ng/ml to 1340 ng/ml with a median of 297 ng/ml. The level of this indicator above 600 ng/ml is interpreted by statistical analysis as emissions in this distribution. In the second group of patients with DM2, a similar pattern was observed in the distribution of the indicator, but the median value of the indicator was at the level of 387 ng/ml and the observed spread of the indicator was 28–1560 ng/ml statistically significantly higher compared with the first group (p<0.001). The values of MMP-9 are characterized in both the first and second groups by a direct correlation with the level of HbA1c. The analysis of pulse wave propagation velocity revealed a statistically significant difference in pulse wave propagation velocity in muscle-type vessels and the CM ratio/SE between patients of the compared groups. Pulse wave propagation velocity for vessels of the classical type was also statistically significantly higher in the group of patients with diabetes mellitus. Conclusions: the determination of MMP9 and pulse wave propagation velocity levels may become an important method for determining the prognosis in patients with DM2 who have undergone STEMI. The analysis of pulse wave propagation velocity revealed a statistically significant difference in pulse wave propagation velocity in muscle-type vessels and the CM ratio/SE between patients of the compared groups. pulse wave propagation velocity for vessels of the classical type was also statistically significantly higher in the group of patients with diabetes mellitus.
3.1.21. PEDIATRICS
A clinical observation of severe combined pathology in a newborn child with congenital hypothyroidism against the background of hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system is presented. Thanks to an early screening examination for congenital hypothyroidism, on the second day of life, the child was promptly prescribed levothyroxine replacement therapy against the background of treatment of concomitant pathology, which led to positive dynamics in the course of the disease and prevented the progression of hypoxic symptoms. ischemic damage to the central nervous system. An adverse effect on the fetus of maternal pathology (acute respiratory viral infection, bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis, bacteriuria) has been demonstrated. The presence of the above factors subsequently led to a severe course of the neonatal period in a child with congenital hypothyroidism and the development of severe concomitant pathology. Early diagnosis of congenital hypothyroidism with immediate prescription of replacement therapy makes it possible to prevent the development of mental retardation in this cohort of newborns. In the future, systematic monitoring of the child by a pediatrician and endocrinologist is required, with dose adjustment of the drug if necessary.
A clinical case of multiple changes in genetic engineering biological therapy in a child with juvenile idiopathic arthritis is presented. A detailed study of this pathology in recent years is associated with an increase in morbidity among the child population, as well as a large number of prognostically unfavorable outcomes of the disease. Particular progress has been made through the use of new approaches in the treatment of arthritis in children. Currently, the use of genetic engineering therapy in the treatment of rheumatic diseases is a highly effective method for reducing disability and improving the quality of life of patients. But at the same time, the issue of starting therapy, choosing a group of biologically active drugs and their timely change in the absence of effect remains relevant. A feature of this clinical case is the timely change in treatment tactics with repeated changes in the class of genetically engineered drugs. Over several years of using GIBP, 6 drugs were used that gave a positive, but short-term effect.
Objective: to analyze the prescribed antimicrobial therapy in young children with non-severe community-acquired pneumonia. Materials and methods: a sample of 219 young children with community-acquired pneumonia admitted to the pediatric department of the State Children's Clinical Hospital №17 in Ufa for the period from September 2022 to August 2023 was formed. Results: the clinical and anamnestic characteristics of children with community-acquired pneumonia are described. Analysis of antimicrobial therapy at the outpatient stage revealed in 51,24% of cases its compliance with clinical recommendations. There was a large share of parenteral drugs (73,97%) in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in a hospital setting. Preference was given to ceftriaxone (43,38%) due to the convenience of the method of administration. Inhibitor-protected aminopenicillins were prescribed half as often (23,29%). Conclusion: The authors believe that well-planned educational interventions will improve the effectiveness of antimicrobial therapy for community-acquired pneumonia in children.
3.2.2 EPIDEMIOLOGY
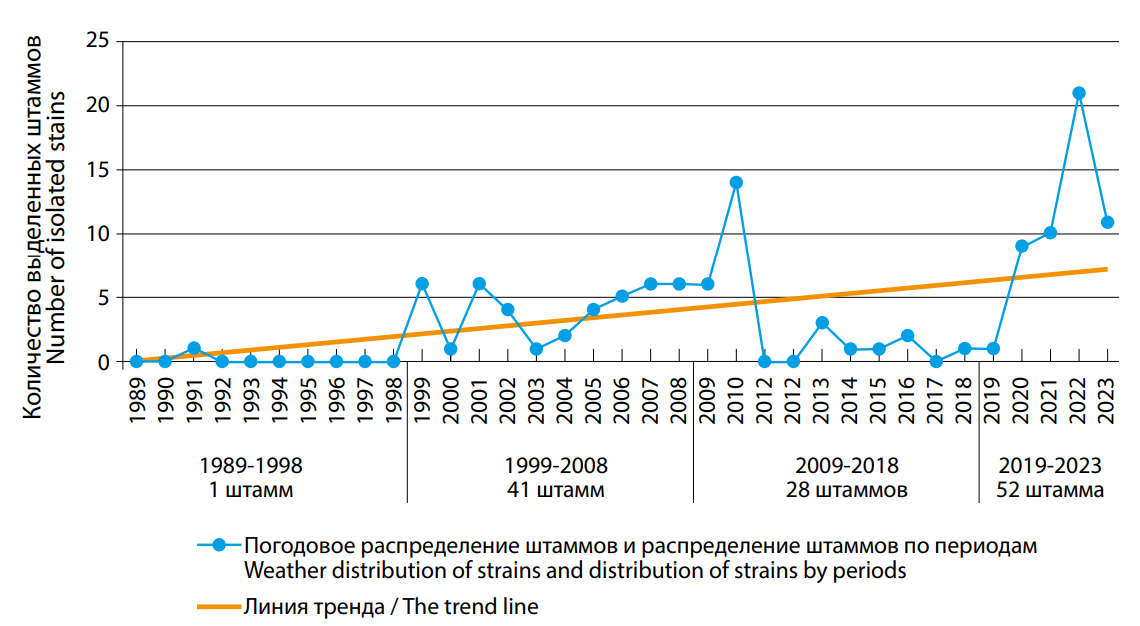
Objective: retrospective analysis of the results of monitoring studies of environmental water bodies in Rostov-on-Don for the presence of V. cholerae for the period from 1989 to 2023 at stationary sampling points assigned to the Rostov-on-Don Anti-Plague Institute of Rospotrebnadzor, identification of trends and features of the dynamics of isolation and biological properties isolated strains. Materials and methods: in the period from 1989 to 2023, 4362 samples from aquatic ecosystems were examined. The organization and conduct of research was carried out in accordance with regulatory and methodological documents (SanPiN 3.3686-21, MUK 4.2.3745- 22, MUK 4.2.3746-22). Sequencing of isolated strains was performed on the MiSeq (Illumina) platform. Results: during the analyzed period, V. cholerae strains were found in all studied reservoirs of the Rostov-on-Don: in the Don, Temernik and Dead Donets rivers, mainly in July and August. Of the 122 isolated strains, 8 are epidemiologically significant (toxigenic strains) and 114 are nontoxigenic. The largest number of strains was isolated in 2022 — 21 strains. V. cholerae strains O1 (119 strains) and O139 (3) of serogroups, biovar classic and El Tor (Ogawa, Inaba and Gikoshima serovars) were found. Conclusions: epidemiological risks of the introduction of the cholerae pathogen from endemic countries, as well as from neighboring countries, in cases of complications of the epidemic of this infection, remain. In the surface reservoirs of the Rostov-on-Don, there are favorable conditions for the circulation of V. cholerae and the risk of spreading infection by water, in case of contamination by the cholerae pathogen of aquatic ecosystems.
Objective: is to analyze the effectiveness of the updated database of the serological monitoring on natural focal dis eases among healthy donors, which allows results accumulation and systematization in order to ensure sanitary and epidemio logical surveillance in the Rostov region. Materials and methods: for database creation we have used the results of the cross sectional studies of the level of the immune layer of the healthy population in the Rostov region during the period from 2020 to 2024 years. Marker indicators for assessing the level of immunity included the determination of immunoglobulins of G and M classes for topical natural focal infections by the immunoenzymometric method. Results: the database was based on Microsoft Office Excel and is used to store, to process and to structure information in a certain way, allowing us to sort and to filter, sup plement data in the process of work, to systematize information and to visualize source data in the form of graphs, diagrams, to conduct statistical analysis of the obtained data and to automate the filling of accounting (reference) documents. Conclusion: the information, which is accumulated in the database, provides quick access to information about regional seromonitoring studies.
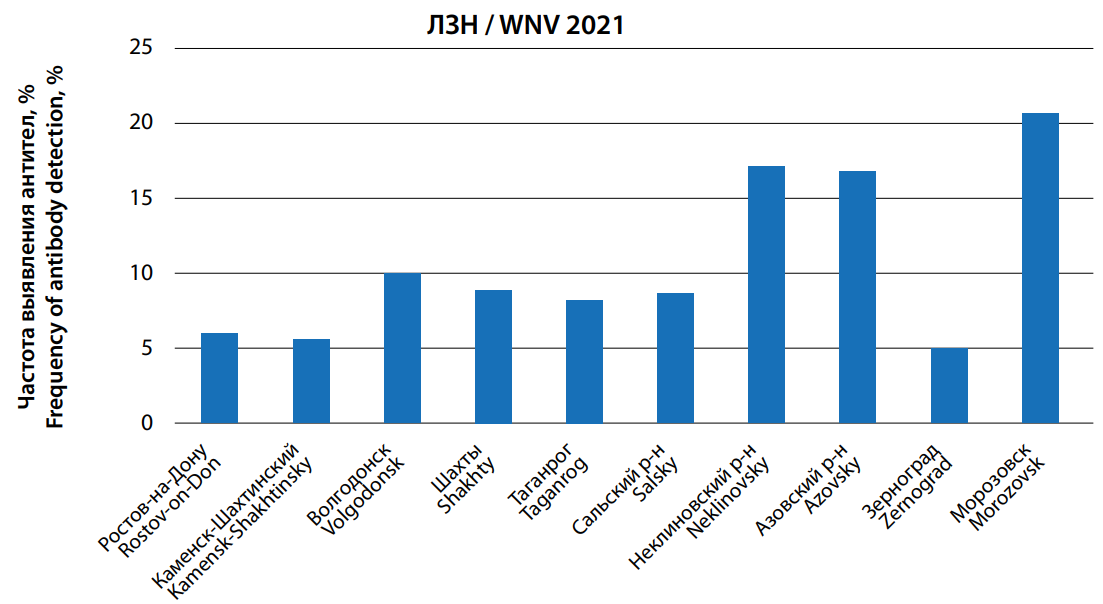
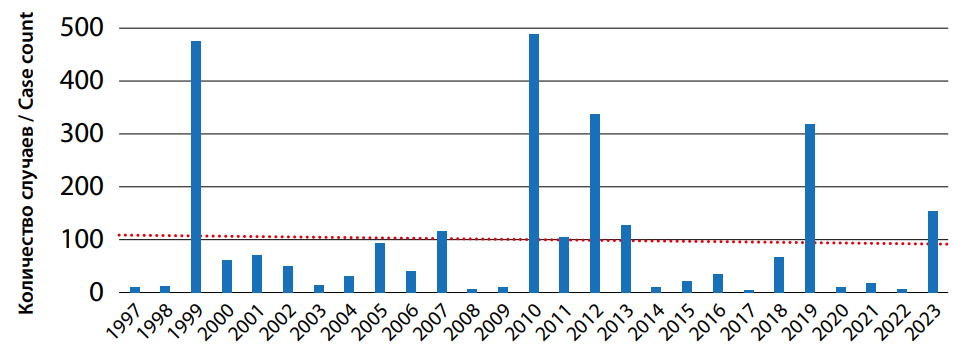
Objective: to study the features of epizootic and epidemiological manifestations of west Nile fever (wNF) in the re gions of the Southern Federal District. Materials and methods: we used data on the registration of cases of the disease and the results of epidemiological surveillance presented in 2009–2023. Directorates of Rospotrebnadzor for the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, archival data, results of their own research, publications and dissertations. Research methods are com plex epidemiological and statistical. The sources of information were: Results: in the Astrakhan, Volgograd, Rostov regions and the Republic of Kalmykia, stable circulation of wNV in the epizootic cycle has been established, in the latter of which epizootic observation data do not correlate with low incidence. In the Krasnodar Territory, the Republics of Adygea, Crimea and the city of Sevastopol, single detections of wNV markers in zoological and entomological material do not allow assessing the intensity and extensiveness of the epizootic process. The epidemic process of wNV in the Volgograd, Astrakhan, and Rostov regions is characterized by almost annual registration of cases with increases in incidence in the interval of 1–7 years, in the Krasnodar Territory - by the outbreak nature of manifestations in some years, in other regions - by sporadic incidence. An upward trend in incidence was noted in the Krasnodar Territory and Rostov Region. The structure of morbidity is dominated by cases of infec tion among men, people aged 60 years and older, urban residents, the clinical picture is a form without damage to the central nervous system and a moderate course. Differences in the epidemiological manifestations of wNV are associated with the pecu liarities of the organization of the epidemiological surveillance system and the influence of territorial social factors. Conclusion: the results can be used in planning and conducting epizootological and epidemiological monitoring, zoning of territories, and development of management decisions.
3.2.7 ALLERGOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Objective: to study the immunological parameters of patients who had suffered from COVID-19 in moderate form 1 and 6 months after recovery. Materials and methods: 60 patients hospitalized with the diagnosis of "COVID-19, moderate form; complication: interstitial pneumonia" were examined. Immunological parameters were assessed 1 month and 6 months after recovery. Comparison group: 20 healthy volunteers. Results: after six months, signs of immune dysfunction continue to persist in the immune status, consisting in a violation of the processes of differentiation and proliferation of immunocompetent cells. Conclusion: the need for immunological monitoring in people who have had COVID-19 for 6 months in order to identify immunodeficiency conditions and prevent infectious diseases against this background is shown.
HISTORICAL OVERVIEW
Objective: on the contribution of anti-plague institutions to ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the country's population. Materials and methods: an analytical review of information from literary sources and databases of Cyberlenink electronic libraries, e-library, as well as archival materials and the library fund of the Institute. Results: the causes and ways of the emergence of the anti-plague system in Russia (hereinafter referred to as the anti-plague service) are outlined, the evolutionary stages of formation are shown, during which the search for the most effective and optimal forms of organiza tion aimed at ensuring a safe epidemiological situation in Russia was carried out. Conclusion: the article contains an assessment of the importance of the work of the Rostov-on-Don Scientific Research Anti-Plague Institute. The main tasks for ensuring pre paredness in case of epidemic complications in Russia are outlined.
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)