REVIEW
Thus, we can talk about the obvious mutual influence between a child with schizophrenia and his mother. On the one hand, it can be manifested in the form of the fact that a certain number of personal characteristics of the mother is accompanied by the formation of high rates of schizoid and neurotic child. Of course, the presence of a certain psychological type of mother (as the only reason) is not enough for the emergence and development of schizophrenia, but the subsequent development of the child’s personal disorders, as a borderline between the norm and pathology, can already be the ground for the development of the disease in the presence of other more significant causes (for example, hereditary). On the other hand, the disease of the child can be a significant stress factor for the mother, leading to the formation of her manifestations of emotional stress and psychological maladjustment, which, in turn, can adversely affect not only the features of her relationship with the child, but also on the features of the course of his disease. The mechanisms of formation of such a «vicious circle» are poorly studied even theoretically, not to mention the fact that in routine psychiatric practice these issues do not fall into the focus of the psychiatrist’s attention, are not taken into account in the development of therapy strategy. However, the parameters of interaction between mother and child, the level of their mutual empathy, can be important for the formation of compliance in the treatment of schizophrenia, as the «conductor» of therapy in relation to a small patient is the mother. There is also no doubt that the level of mental health of the mother is an important resource for maintaining the viability of the whole family system and, in particular, a necessary condition for the organization of adequate therapy for a child with schizophrenia. Therefore, the study of the issues of mutual influence of the patient with schizophrenia and his mother, the development of ways to correct the problems arising in this case are an important scientific and practical task of modern psychiatry.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Objective: to evaluate and compare the influence of the options for the induction of general anesthesia for elective abdominal delivery on the condition of newborns.
Materials and Methods: The study included 160 newborns, which were born via elective cesarean section under general anaesthesia. All newborns were divided into 4 groups, 40 in each, depending on the anesthetics used for the induction of general anesthesia. In the 1st group, thiopental sodium 5 mg/kg was used; in the 2nd - sodium thiopental 7 mg/kg; in the 3rd - propofol 2,5 mg/kg; in the 4th- sodium thiopental 5 mg/kg with sevoflurane (0,5 MAC). The influence of anesthesia on condition of newborns was evaluated by the Apgar scale and the neurological and adaptive capacity scale NACS.
Results: statistically significant differences were not found in assessing newborns on scales.
Conclusion: All the researched drugs and their doses used for the induction of general anesthesia during elective abdominal delivery do not adversely effect on the neurological and somatic status of the newborn.
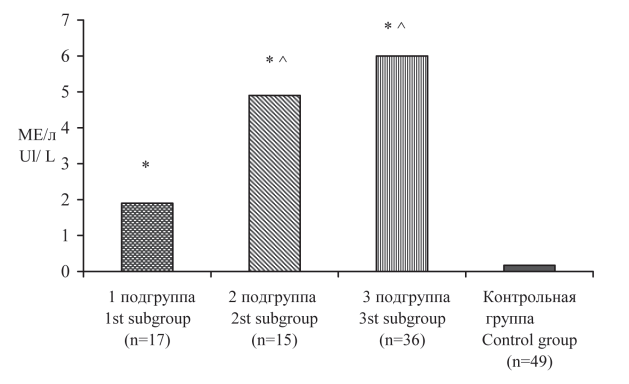
Objective: to study the functional state of the thyroid gland in newborns from mothers with diffuse toxic goiter, depending on the level of antibodies to thyroid stimulating hormone receptors (AB-rTSH).
Materials and methods: 68 newborns from 67 mothers with diffuse toxic goiter were examined. The control group included 49 newborns from 49 mothers without thyroid pathology. To assess the functional state of the thyroid gland of newborns, we determined the levels of thyroid stimulating hormone, free thyroxine (fT4), and AB-rTSH in cord blood and calculated the TSH/fT4 coefficient, which allows us to differentiate congenital hypothyroidism from neonatal thyrotoxicosis. On the 4-7th day of life, all newborns underwent ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the thyroid gland.
Results: newborns from mothers with diffuse toxic goiter had lower growth-weight indices in comparison with the same indices of the control group and they often showed thyroid hyperplasia. It was shown that the increased content of AB-rTSH in the blood serum of pregnant women with diffuse toxic goiter and in the umbilical cord blood of newborns can contribute to the development of neonatal thyrotoxicosis, detected in 16.2 % of newborns.
Conclusions: increased levels of AB-rTSH in the blood serum of mothers with DTG, especially in the second half of pregnancy, and in the umbilical cord blood of newborns affect the formation of thyroid hyperplasia in newborns and contribute to the development of neonatal thyrotoxicosis.
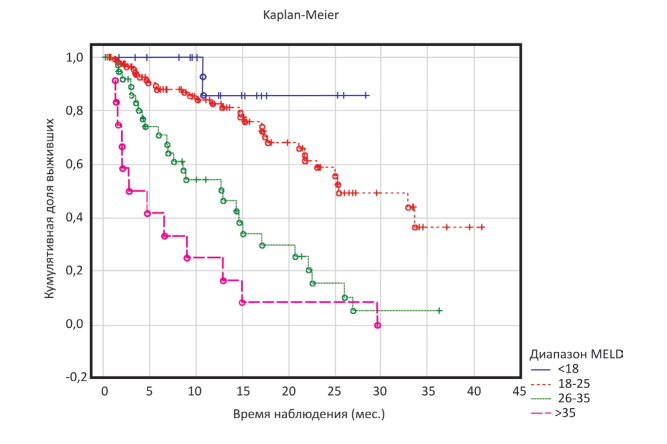
Purpose: analysis of various clinical results in patients registered in the liver transplantation waiting list (LTWL).
Materials and methods: the study was carried at the Center of Surgery and Donor Coordination of the Rostov Regional Clinical Hospital using clinical, laboratory and instrumental data of 198 patients from the LTWL. 99 men and 99 women were enrolled into this study. The men age ranged from 21 to 70 years (47.8 ± 10.4 years), women age - from 18 to 66 years (49.2 ± 10.9 years). At the time of analysis of the LTWL, the average follow-up period was 14.8 ± 11.2 months. All patients were examined according to the list required for inclusion in the LTWL.
Results: depending on the outcome, 198 patients from TLWL were grouped into 4 groups. The first group (delisting group) — 19 patients (9.6 %) with clinical and laboratory indicators that allowed them to be excluded from WL. The second group — 67 patients (33.8 %) who had positive clinical dynamics following therapy. The third group — 39 patients (19.7 %) who underwent liver transplantation. The fourth group — 73 patients (36.9 %) who had negative dynamics following therapy, including patients with a fatal outcome. While keeping LTWL for 4 years, 61 (30.81 %) of 198 listed patients died. The majority (40 patients) died of bleeding from varicose veins and OPPN, 17 patients died of hepatic coma and SPB. Each group represents the distribution of patients according to the MELD-Na scale, the severity of portal hypertension and hepatic encephalopathy.
Conclusion: the following factors are indispensable for successful work of the transplant center: systematic work with the territories in order to expand the donor base; defining the patient priority criteria in the LTWL in order to reduce the death rate in the list; detailed examination of the patient before entering the list; forming the observation base; systematic patient observation during the pre- and postoperative period, at the rehabilitation stage, as well as at long-term periods in order to develop an effective algorithm of management of the recipient of a solid organ.
Objective: to study the clinical neuropsychiatric and neuropsychological features of children suffering from systemic somatovegetative disorders.
Materials and methods: the study involved children from 5 to 12 years old with an established diagnosis of bronchial asthma — 108 children; atopic dermatitis — 105 children; gastroesophageal reflux disease — 112 children; the control group consisted of 60 same age healthy children. All children underwent clinical-anamnestic, neurological, psychopathological and neuropsychological research.
Results: the children with systemic somatovegetative disorders have a significantly high incidence of pathogenic factors of central nervous system damage in early stages of ontogenesis (pathology of pregnancy and childbirth). Early sensory and motor deprivation due to somatic suffering aggravates neuropsychiatric deficiency. Neuropsychological disorders were predominantly represented by a violation of the perception of their body, lack of kinesthetic and motor functions, spatial and quasi-spatial representations.
Conclusion: the clinical dynamics of neuropsychiatric disorders in children with systemic somatovegetative disorders corresponds to the dynamics of residual cerebral organic impairment with a stage-age changes of syndromes. The revealed neuropsychological disorders correspond to preferential damage to the first (energy) functional block of the brain.
Objective: to analyze the incidence of community-acquired pneumonia and acute otitis media in children during the first four years of life in different age groups vaccinated with pneumococcal 13-valent vaccine Prevenar.
Materials and methods: medical records of 590 children aged 1 to 5 years were analyzed. All subjects were divided into 2 groups. The first group consisted of vaccinated children (n = 490), born in 2014, and vaccinated against pneumococcal 13-valent vaccine Prevenar. The second group consisted of unvaccinated children (n = 100) born in 2013 and not vaccinated. Each group was divided into subgroups depending on the age period (1—2 years, 2—3 years, 3—4 years, 4—5 years).
Results: it is established that the conduct of specific prophylaxis of pneumococcal infection vaccine Prevenar-13 in children during the first 4 years of life effectively reduces the incidence of community-acquired pneumonia (in 7,6 times) and acute otitis media (in 8,5 times). The effectiveness of the vaccine was observed in all age groups. In cases of development of an inoculated child acute otitis reduces the risk of severe forms and complications of the disease. Analysis of the course of the post-vaccination period indicates a high level of safety and good tolerability of the vaccine.
Conclusion: Implementation of specific prophylaxis of pneumococcal 13-valent vaccine Prevenar in children during the first four years of life according to the calendar of vaccination effectively reduces the incidence of community-acquired pneumonia (87 %) and acute otitis media (42,8 %) in all age subgroups. In cases of development of an inoculated child acute otitis reduces the risk of severe forms and complications of the disease. Analysis of the course of the post-vaccination period indicates a high level of safety and good tolerability of the vaccine.
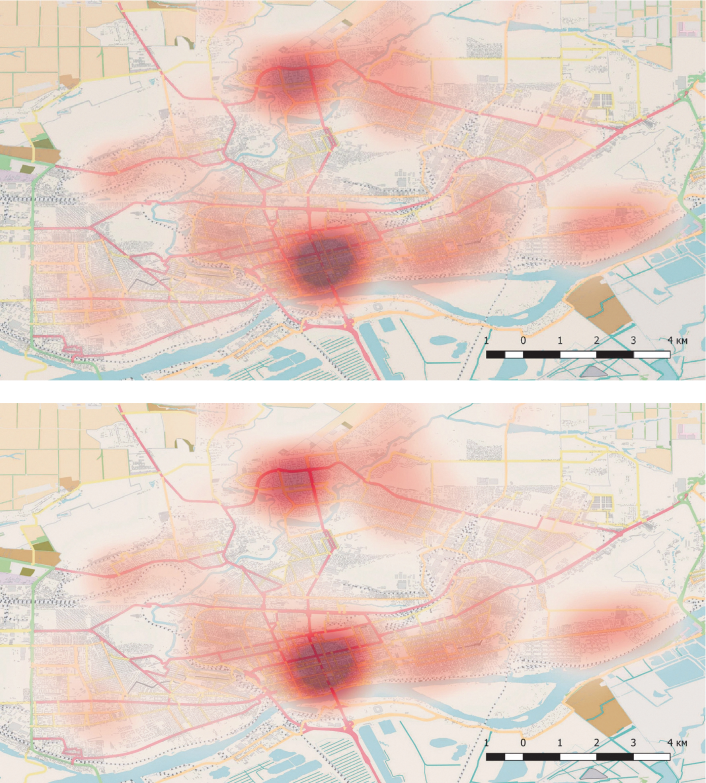
Objective: the assessment of spatial distribution of influenza in the metropolis and creation of the geographic information system (hereinafter – GIS) « Influenza: Rostov-on-Don «, containing data on places of case registration.
Materials and methods: statistical data on influenza cases based on primary and final reports, PCR studies were used. Geocoding of addresses was performed using the servers Nominatum and the Satellite. For development of GIS we used free software QGIS version 3.2.2. As the cartographic basis OpenStreetMap community maps were used.
Results: construction of variograms («heat maps») revealed the formation of several risk areas («epidemiological spots»), the boundaries of which do not coincide with the boundaries of the administrative districts of the city.
Conclusions: the analysis showed that distribution of each of the subtypes of influenza A virus in the territory of Rostov-on-Don in the 2018-2019 season has specific features. We showed that in conditions of the megalopolis the spatial analysis which was carried out without taking into account the administrative boundaries provided more accurate results in comparison with traditional zoning.
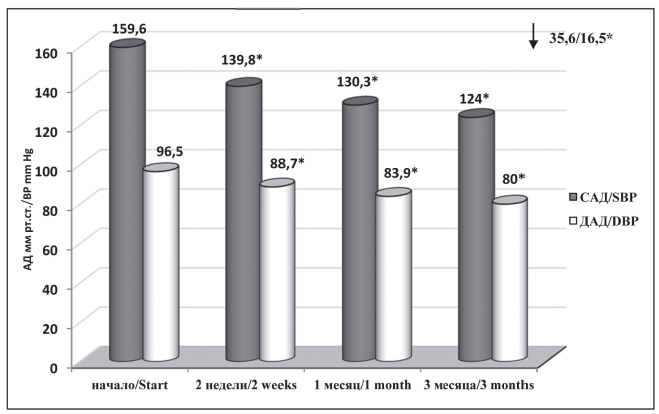
Objective: to study the antihypertensive efficacy of a new dosage form of perindopril A — tablets dispersed in the oral cavity — in the group of patients with arterial hypertension (AH) on an outpatient basis.
Material and methods: the study included 30 patients (mean age 53.8 ± 0.9 years) with the presence of arterial hypertension, diagnosed initially, or with no control of blood pressure at the background of previous antihypertensive therapy. All investigators were administered perindopril A in the form of a dispersible form in a dose of 10 mg in monotherapy or in combination with indapamide – in case of failure to achieve target blood pressure after 2 weeks of observation. The total duration of the study is 3 months.
Results: by the end of the observation, the SBP / DBP decreased by 35.6 ± 2.3 / 16.5 ± 1.0 mm Hg. Correction of therapy with the addition of indapamide-retard was required in 6 (20%) patients. Effective antihypertensive therapy was accompanied by a significant decrease in daily (according to ICBP data), intravisit, and visit-to-visit variability of the SBP, which was 4.4 mm Hg in terms of standard deviation by the end of the observation. The use of a new dosage form of perindopril A was accompanied by a significant increase in adherence to therapy.
Conclusion: the use of a new dosage form of perindopril A — tablets dispersed in the oral cavity — in monotherapy or in combination with indapamide-retard can improve the treatment of patients with hypertension who do not have target BP values.
Objective: to develop tactics for the differential diagnosis of paraneoplastic neuromuscular syndromes in patients at the outpatient level.
Materials and methods: the study included 50 patients with classical neuromuscular paraneoplastic syndromes (experimental group) and 50 patients with neuromuscular syndromes of non-paraneoplastic nature (control group). All patients underwent a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination at the Regional Consultative and Diagnostic Center of the Ministry of Health of the Rostov Region from 2014 to 2018.
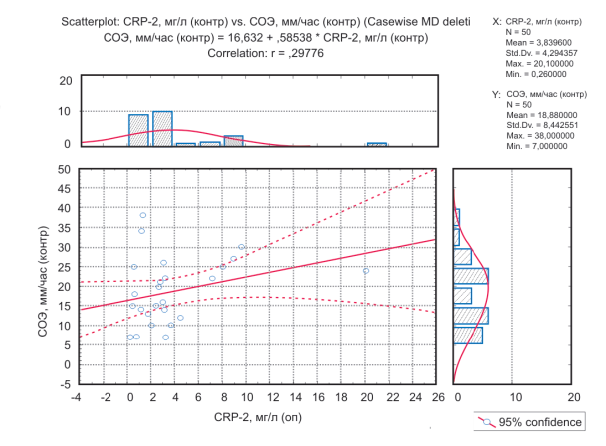
Results: the evaluation of clinical differences in patients of the experimental and control groups was created. When comparing the laboratory parameters, it was revealed that the SFMC, D-dimer, CRP-2 levels significantly increased in patients with paraneoplastic lesions (p <0.05). In the experimental group, a significant increase in the amplitude of the M-response from the sensory nerves (> 5.25 mV) was noted. Based on obtained data, differential diagnosis algorithms for patients with studied neuromuscular lesions at the outpatient level have been developed.
Conclusions: the conducted study allows the implementation of non-serological diagnostics algorithms for classical neuromuscular paraneoplastic syndromes in outpatient practice.
Objective: to study a role of the rs5219 polymorphism in KCNJ11 in the formation of the response variability to vildagliptin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Materials and methods: 48 patients with newly diagnosed T2DM were examined. For all patients vildagliptin in a dose of 50 mg/day was prescribed. If necessary, dose titration was carried out or other glucose-lowering therapy was prescribed for 6 months of observation. Dynamics of the main indicators of glycemic control and body mass index were studied, presence of the rs5219 polymorphism in KCNJ11 gene was also determined.
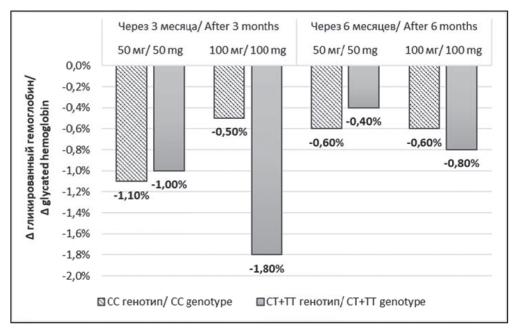
Results: all patients-carriers the T allele had achieved the target values of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in 3 months of vildagliptin monotherapy, compared to patients with wild-type gene who achieved target values of HbA1c in only 44,4% of cases. Increasing the dose to 100 mg/day required 35% of patients with wild-type gene and 17.9% of patients with rs5219 polymorphism. The appointment of a combination of glucose-lowering therapy was necessary in 40% of patients with the wild-type gene and no one with polymorphism.
Conclusion: the presence of the polymorphic allele T rs5219 in KCNJ11 gene makes it possible to predict the high efficacy of vildagliptin monotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed T2DM.
EXPERIENCE EXCHANGE
Objectives: to analyze the prevalence of strains of gram-negative bacteria - pathogens of infectious complications resistant to carbapenems, including through the production of carbapenemases isolated from various clinical biomaterials in hospitalized patients of hospitals in the city of Rostov-on-Don.
Materials and methods: 366 gram-negative bacterial isolates were studied, from patients from 16 wards, 9 treatment-and-prophylactic institutions of the city of Rostov-on-Don and the region. The study was conducted by traditional microbiological method. Species identification of strains and sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs were determined on a Vitek 2 automatic analyzer (BioMerieux, France). The strains insensitive to carbapenems were tested for the presence of carbapenemases using CIM-test. MBL was detected by the effect of suppression of their activity in the presence of EDTA. MBL genes were detected by PCR-RV test kit “AmpliSens MDR MBL-FL”, “AmpliSens MDR KPC/OXA-48-FL”. The conclusion about the production of BLRS was made by the presence of synergism of cephalosporins of III-IV generation with clavulanic acid by the method of double discs.
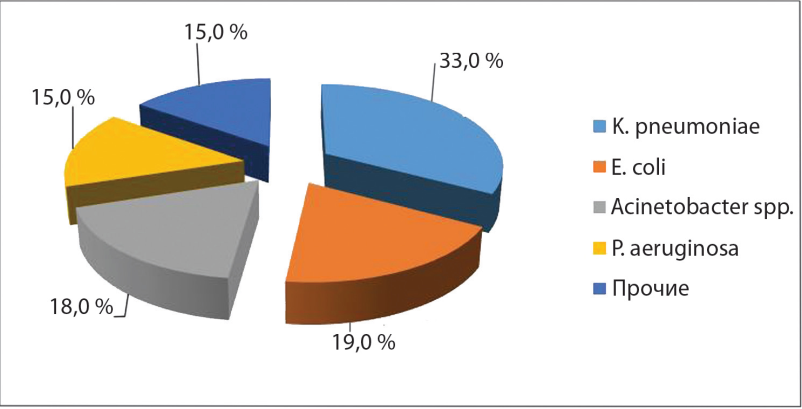
Results: of the 366 isolates tested, gram-negative bacteria accounted for 74.2 %: Klebsiella pneumoniae — 33.0 %, Escherichia coli — 19.0 %, Acinetobacter baumannii — 18.0 %, Pseudomonas aeruginosa — 15.0 %. Resistance to carbapenems was detected in 90.9 % of A.baumannii strains, more than 50 % of P.aeruginosa and K.pneumoniae. LBR production was detected in more than 90 % of K.pneumoniae and about 80 % of E. coli. In A. baumannii and K.pneumoniae isolates, the presence of OXA and NDM genes was found, and in P.aeruginosa, VIM groups.
Conclusion: enterobacteria resistant to beta-lactams, producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and carbapenemases are one of the leading causative agents of infectious complications in hospitals of Rostov-on-don and the region, almost not inferior in frequency of occurrence of bacteria of the genus Acinetobacter spp. and Paeruginosa. This determines the importance of detection of resistance mechanisms not only for the purpose of optimal etiotropic therapy, but also for epidemiological control of the spread of resistant strains and the development of infection control measures.
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)