REVIEW
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Objective: epidemiological analysis of myelodysplastic syndrome, based on the available retrospective data.
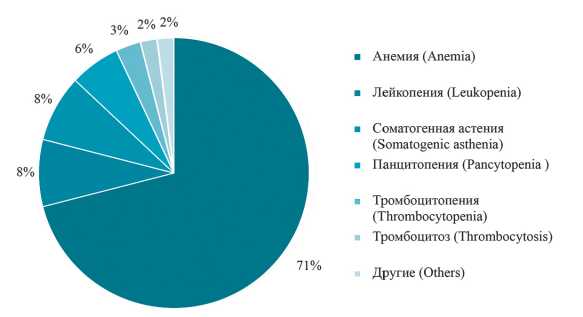
Materials and methods: a retrospective analysis of the medical history data of 115 patients (61 men and 54 women) with a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome who received treatment in the hematology department of the «City Hospital № 7 of the city of Rostov-on-Don» in the period from 2010 to 2019.
Results: the most likely comorbidities were cardiovascular diseases, which are the main cause of sudden death, and endocrine diseases, which together influence the outcome of myelodysplastic syndrome.
Conclusions: there are no individual risk assessment algorithms that could determine the goal setting of therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome, whose life expectancy depends more on the course of concomitant diseases.
Objective: to investigate the heart rate variability (HRV) parameters of patients with a stable angina pectoris depending of presence depressive disorders; to identify the influence of affective symptoms on the clinical outcome during 12 months of observation.
Material and methods: there are 121 male patients included in research with a stable angina pectoris II – III functional classes, hospitalized for a drug treatment and planned percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with stenting. The severity of affective symptoms and HRV are being assessed.
Results: patients with depressive symptoms in the conservative treatment group had low SDNN level; patients with psychoemotional disorders in the surgical treatment group had differences by all HRV parameters (SDNN, SDANN, SDNN, rMSSD pNN50). Clinically unfavorable outcome, including intermediate points such as increase in angina attacks, re-hospitalization, stent’s restenosis, were mostly registered during 12 months of observation in the groups with affective symptoms.
Conclusions: presence of depressive symptoms of patients with stable angina pectoris is accompanied with low HRV parameters, which is connected with worsening of cardiac prognosis.
Objective: to study the state of cytokine status in children with acute and chronic urticaria.
Materials and methods: 264 children of both sexes aged from 6 to 16 years with different variants of urticaria were examined. Clinical research methods included analysis of anamnestic data, objective examination of the child to determine the severity of urticaria. Immunological research methods included determination of IL-4, IL-6, IL-17, and IFN-γ levels by the method of enzyme immunoassay of blood serum.
Results: cytokine profile analysis revealed hyperproduction of IL-17, γ-IFN with reduced IL-4 synthesis in children with acute urticaria. In children with chronic urticaria, IL-6 hyperproduction is noted against the background of a significant decrease in IL-4 synthesis.
Conclusion: there was a significant relationship between the development of severe acute urticaria and the levels of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-17, and between the formation of chronic urticaria and the level of IL-6.
Objective: study of associations between VDR gene rs1544410 and rs10735810 polymorphisms, MCM6 gene rs4988235, CALCR gene rs1801197 one and ibandronate efficacy in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Materials and methods: 117 women with postmenopausal osteoporosis were examined for 12 months in the dynamics of treatment with ibandronate. Evaluation of therapy effectiveness was based on indicators of increase in bone mineral density in L1-L4 lumbar vertebrae, as well as left and right femurs.
Results: An association of GG genotype of VDR gene rs1544410 polymorphism with low growth rates of mineral density of L1-L4 lumbar vertebrae (3,41 ± 0,60 % versus 5,51 ± 0,78 % in other women; р = 0,036) was established. The effect of other studied polymorphisms (rs10735810 of VDR gene, rs4988235 of MCM6 gene, rs1801197 of CALCR gene) on treatment effectiveness was not found.
Conclusion: it is advisable to use obtained results when developing personalized regimens for antiresorptive therapy for women with postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Objective: to evaluate the effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockers on aldosterone level in patients with chronic heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Materials and methods: the prospective study included 158 patients (58 men and 100 women, mean age 62,3 ± 7,4 years) with HFpEF (> 50 %) and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction. All patients had no history of primary aldosteronism and did not use the mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists during the last 6 weeks. We evaluated the duration of treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin-2 receptor antagonists (ARA-2) and its average daily dose. The dose of RAAS blockers was assessed during previous 6 months as a percentage of target. Aldosterone plasma concentration was measured and the normal level was 40 – 160 pg/ml.
Results: according to laboratory results 99 patients (62,7 %) had normal aldosterone level (nAld) and 59 patients (37,3 %) had high aldosterone level (hAld). hAld patients had significantly higher duration of RAAS blockers treatment (6 (3; 8) versus 4 (2; 5) years, p < 0,001) and dose (50 (25; 50) % vs 25 (12,5; 50) % of target, р=0,01). Multiple regression analysis showed that after standartization for age, severity of HFpEF, duration of arterial hypertension and comorbidity only long-term (more than 5 years) treatment with RAAS blockers remained the independent risk factor of high aldosterone level (odds ratio 3,16, 95 % confidence interval 2,08 – 8,24).
Conclusions: in HFpEF patients’ plasma aldosterone level is closely associated with RAAS blockers treatment. Long-term (more than 5 years) therapy with ACE inhibitors or ARA-2 is the independent risk factor of secondary hyperaldosteronism.
CASE REPORT
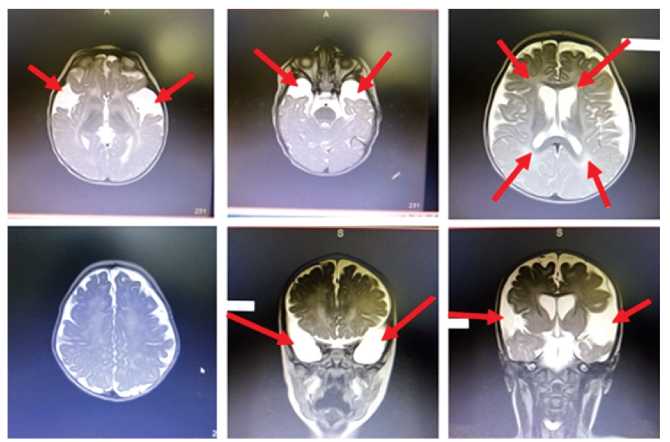
Glutaric aciduria type I (deficiency of glutaryl-COA dehydrogenase, glutaric acidemia type I) is a rare autosomal recessive disease caused by mutations in the gene encoding the enzyme glutaryl – COA - dehydrogenase (GCDH). Cerebral organic aciduria, caused by a deficiency of glutaryl-COA - dehydrogenase, is generally considered a neurological disorder.
The phenotypic spectrum of untreated GA-1 varies from a more common and pronounced form (a disease with infancy) to a low-symptom and less common form. In people with the same genotype, the clinical manifestations and depth of CNS damage can vary widely depending on the age of manifestation of acute encephalopathic crises. It is assumed that with early detection and treatment of “asymptomatic” newborns (in the context of screening for this disease), most people who would have developed manifestations of GA-1 with childhood or late onset will remain asymptomatic.
EXPERIENCE EXCHANGE
Objective: analyze the validity of destructive treatments for cervical diseases in clinical practice.
Materials and methods: analyzed archival medical documentation (medical records of an inpatient patient, form 003/y) of 258 patients who underwent surgical treatment of cervical diseases in 2017 – 2018. Statistical data were calculated on a personal computer using the Microsoft Excel 2011 for Mac program and the «Statistica» statistical program.
Results: an analysis of medical documentation revealed that a complete set of diagnostic methods, regulated by the clinical recommendations “Benign and precancerous cervical diseases from the perspective of cancer prevention” (2017), including HPV genotyping, was carried out in 28.7 % women. Before surgical treatment, a cytological examination of the cervix was carried out in 89.5 % cases, HPV-test — 31.4 % patients. As a result of the comparison of 258 histological and pre-operative clinical diagnoses, overdiagnosis of low- and high-grade cervical lesions (LSIL and HSIL) was noted in 16 (23.2 %) patients who did not have a history of childbirth and 42 (22.0 %) women who had previously given birth, which determined the use of destructive treatments without indications in 58 (22.5%) cases. An underestimation of the severity of cervical damage among unborn patients was found in 9 (13.0 %) patients, as well as in 40 (21.2 %) women with a history of childbirth.
Conclusions: overdiagnosis of the degree of intraepithelial cervical lesions entails the unreasonable use of destructive methods of treatment in young unborn women who violate the anatomic-functional integrity of the cervix and the architectonics of the cervical canal.
Purpose: to analyze the epidemiological situation for a new coronavirus infection (COVID-19), to identify some regional features of the Rostov region that contribute to spread of infection.
Materials and methods: when assessing the epidemiological situation for a new coronavirus infection in the Rostov region, we used information provided by the Department of the Federal service for supervision of consumer protection and human welfare in the Rostov region. Processing of statistical data was performed by means of generally accepted method.
Results: the spreading of a new coronavirus infection in the Rostov region is uneven in nature. When differentiating the territories of the region we identified groups of municipalities with a very high, medium and low number of patients. The administrative territories division of the Rostov region into the “Rostov urban agglomeration” and cluster of municipalities in which pronounced factors and conditions determining the “pendulum” migration of the population are absent, allow analyzing the specific features of the region and identification of territory with the highest risk of epidemic process intensification of a new coronavirus infection.
Conclusions: the carried out differentiation of municipalities made it possible to identify and analyze some territorial features of the Rostov region, contributing to the spread of a new coronavirus infection. The obtained results could be used for development of measures aimed at reducing intensification of the epidemic process COVID-19 in condition infection.
Objective: to evaluate the behavioral risk factors of the workers of the primary oil refining workshop with the aim of using them as a tool for substantiating management decisions and forming vectors of preventive measures.
Materials and methods: the method of active survey investigated the prevalence of behavioral risk factors among operators in two age groups (20 – 35 and 36 – 60 years old).
Results: the main vectors of behavioral risks for operators of different age groups were established: lack of motor activity, smoking, low medical activity, low perception of behavioral risks. Violations of lifestyle are predominantly combined (violations by 2 – 4 indicators). For older operators are more characterized by low motor and medical activity, disturbances in diet, an overestimation of the degree of influence of environmental and occupational factors on health when the significance of individual behavior is underestimated.
Conclusions: Social policy at the enterprise should take into account the main vectors of behavioral risks, lower motivation and the implementation of a healthy style of behavior typical of older workers.
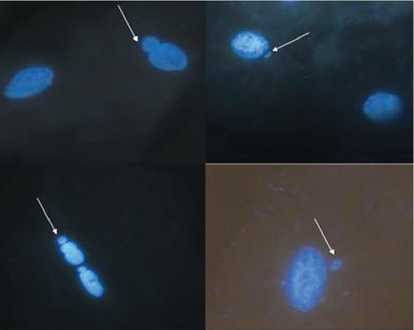
Purpose: to determine the relationship of the damage level of cell genetic apparatus with reproductive health disorder degree under conditions of harmful production.
Materials and methods: the study involved 36 poultry farm female workers of childbearing age. The first group was made up by 22 workers of the main production. The control group included the other 14 employees who were administrative and managerial personnel. Clinical statistical study of reproductive health was carried out with simultaneous investigation of the cariological indices of buccal epithelium using a fluorescence microscope. At least 1000 cells in a monolayer were analyzed on each micropreparation. Statistical data analysis was made using Statistica 6.0.
Results: in workers of the main production, there was a high spread of inflammatory gynecological diseases (90.9 % versus 57.1 % in the control group), uterine fibroids (9.1 %, versus 7.1 %). At the same time a statistically significant increase in the number of cells with micronuclei was revealed in this group by 2.6 times (p < 0.05), with protrusions by 1.8 times (p < 0.05), an increase in the total proliferation index by 2.3 times (p < 0.05), and the two-nuclear cells made the greatest contribution to these differences. The integral indicator of cytogenetic disorders of women of the 1st group was also significantly higher by 2.0 times (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: negative influence of factors of poultry house production environment on cell genome stability disturbance was revealed. It has been established that the reproductive health disorder degree has a direct proportional dependence on the damage level of cell genetic apparatus.
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)