EPIDEMIOLOGY
An epizootological inspection of the liberated territories of the Donetsk and Lugansk People's Republics, Zaporozhye and Kherson regions was carried out. It was established that the faunal complex of small mammals, hare-like and ectoparasites, as well as their number, make it possible to ensure the circulation of natural focal infections identified by the results of laboratory studies: tularemia, Crimean hemorrhagic fever (CHF), West Nile fever (WNF), ixodic tick-borne borreliosis (ITB), rickettsiosis, human granulocytic anaplasmosis (HGA), leptospirosis, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS), Q fever, intestinal yersiniosis, Batai, Inco, Sindbis, Tyaginya fevers. For the first time, the PCR method in field material from the Zaporozhye region (Berdyansk and Melitopol regions) detected the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, on the territory of the Donetsk and Lugansk People's Republics in the populations of small mammals (rodents and insectivores), the circulation of viruses Inco, Sindbis, Tyagin, Batai was established. In the territories of Kherson and Zaporozhye regions, the presence of combined and conjugated natural foci of ixodic tick-borne borreliosis, rickettsiosis and human granulocytic anaplasmosis is determined. According to the results of molecular genetic analysis, it was shown that the causative agents of natural focal infections (Crimean hemorrhagic fever, West Nile fever, ixodic tick-borne borreliosis, rickettsiosis) identified in 2023 are genetically close to strains circulating in the regions of the south European part of Russia.
Objective: to study the level of the immune layer of the population to pathogens of natural focal infectious diseases in order to establish the epidemic activity of natural foci of particularly dangerous infectious diseases in the Rostov region.
Materials and methods: blood serums of healthy donors living in the administrative territories of the region were collected in the period from 2020 to 2022. Specific antibodies in blood sera were determined by the ELISA method. Serum specific IgG class immunoglobulins were used as a serological marker of the transmitted infection.
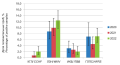
Results: IgG to the Crimean hemorrhagic fever virus was not detected in 2020. In 2021, the share of seropositive results was 0.7%, in 2022 — 2.0%. The proportion of IgG to West Nile virus in 2020 was 8.7%, in 2021 — 9.9%, in 2022 — 12.4%. Serological testing revealed an immune layer to ixodic tick–borne borreliosis in 2020–2022: 3.1%, 2.6% and 2.0%, respectively. Antibodies to hantaviruses, pathogens of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in the blood of residents of the region in 2020 were found in 7.0% of samples, in 2021 — 4.5%, in 2022 — 7.1%. The share of positive samples in the study for Ku fever in 2022 was 2.3%. Conclusion: Seropositive samples were detected for all studied natural focal infections. The greatest variety of natural focal infections confirmed by serological monitoring data was detected in cities (Rostov-on-Don, Taganrog, Zernograd, Kamensk-Shakhtinsky) and districts of RO (Salsky, Neklinovsky, Remontnensky).
Conclusion. The results of the serological monitoring made it possible to identify the circulation of pathogens of KGL, LZN, ICB, Ku fever, hantaviruses in the territory of two districts of the region. The detection of specific antibodies in the blood sera of healthy donors indicates the epidemic activity of natural foci. Also, a comprehensive study of healthy donors expanded the understanding of the area of the most relevant natural focal infections such as (KGL, LZN, ICB), and less frequently registered at present (HFRS and Ku fever).
Objective: to assess the epidemic situation of echinococcosis in the period 2012–2022 in the endemic territories of the Far Eastern Federal District and South of Russia.
Materials and methods: based on the data of the annual statistical reporting forms No. 2 "Information on infectious and parasitic diseases", data from the Reference Center for Monitoring Larval Helminthiasis of Rostov Research Institute Microbiology and Parasitology of Rospotrebnadzor, an analysis of the incidence of echinococcosis in the territories of the Far East and South of Russia in the period 2012–2022 was carried out. For seroepidemiological examination of a conditionally healthy population by the ELISA method, the diagnostic kit "Echinococcus-IgG-ELISA-BEST" (JSC "Vector-Best", Novosibirsk) was used.
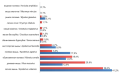
Results: it is shown that the epidemiological situation of echinococcosis is characterized by pronounced territorial unevenness. In the south of Russia, epidemiological problems with echinococcosis persisted in Kalmykia (0.74–2.19 cases per 100,000 population) and in the Astrakhan region (0.60–1.48 cases per 100,000 population). Among the relatively healthy population, the average seropositivity to E.granulosus antigens in the Far East was 5.8%, in the south of Russia — 2,6%. Conclusions: the data obtained indicate an unfavorable epidemiological situation for echinococcosis in a number of regions of the Far East and South of Russia.
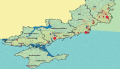
Objective: to evaluate the role of blood-sucking mosquitoes of various species living in the northern and central regions of the Crimean Peninsula in the transmission of West Nile virus (WNV).
Materials and methods: the collection of bloodsucking mosquitoes was carried out in 7 administrative units of the Republic of Crimea with automatic traps and a vertical handheld vacuum cleaner from July 1 to August 5, 2022. The species composition of mosquitoes was determined visually using an MSP-1 stereomicroscope (option 22) using standard keys. Detection of WNV RNA in the samples was performed by RT-PCR. Mosquito infection levels and dominance index were calculated.
Results: a common eudominant species for urban and rural biotopes of the surveyed areas was determined Ae. caspius, whose dominance index was 72.4% and 31.3%. Mosquitoes of the species Cx. modestus were the most numerous in rural biotopes (dominance index — 48.4%). The invasive species Ae. albopictus in the central part of the Crimean peninsula, which indicates the expansion of its habitat. Of 18.6 thousand mosquitoes of 12 species, merged in 693 samples, WNV RNA was detected in 14 samples (2.02%), 3 isolates of the pathogen were isolated. A high level of WNV infection of mosquitoes in urban biotopes was established, which amounted to 4.12%. WNV circulation was first confirmed in the northern part of Crimea (Krasnoperekopsky district).
Conclusion: the epidemiological significance of mosquitoes of various species on the territory of the Crimean Peninsula has been determined. The data on the spread of WNV in the Republic of Crimea were supplemented, taking into account which the estimated zoning of the territory was carried out according to the degree of risk of infection with WNV. Recommendations are given to strengthen epidemiological surveillance and preventive measures.
Objective: to analyze the incidence of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) in healthcare settings of the Rostov region and the risks of their occurrence in order to develop proposals for improving the complex of anti-epidemic and preventive measures to prevent HAIs in healthcare settings of the Rostov region at present.
Materials and methods: the materials for the work were data from reports "On the state of sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population in the Rostov region" during 2009–2022, inspection reports and instructions from officials of the Department of Rospotrebnadzor in the Rostov region, expert opinions of specialists from the filial of the Federal Budgetary Healthcare Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Rostov Region" in Rostov-on-Don on selective inspection of healthcare setting in 2021-2023. The work used an operative and retrospective epidemiological analysis.
Results: the results of the analysis of the incidence of HAIs and the risks of their occurrence in healthcare settings of the Rostov region distinctly demonstrated the relevance of the problem of HAIs. To ensure the safety of medical care in the Rostov region, additional professional training programs about prevention of HAIs have been developed for medical workers.
Conclusion: the results obtained made it possible to identify the risks of HAIs and propose specific measures to improve the complex of anti-epidemic and preventive measures to prevent HAIs in healthcare settings of the Rostov region.
Objective: to analyze the rate of treatment demand after contact with animals in the Omsk region.
Materials and methods: we used data of rate of treatment demand of Omsk region population due to injuries caused by animals in 2009–2022. A descriptive-evaluative epidemiological research method was used. The characteristics of injuries from domestic owned (dogs and cats with an owner), domestic stray (stray dogs and cats) and wild (including synanthropic rodents) animals are analyzed.
Results: in 2009–2022 in the Omsk region, 65142 people were injured by animals, which amounted to an average of 4653 complaints per year. Appeals from children aged 0–17 years old amounted to 36,5%, and from children aged 0–14 — 30,2% of the total. The leading role belongs to injuries caused by domestic animals — 67,1%, and of these, in 75,4% of cases — by dogs. An increase in calls regarding attacks by stray dogs has been established and is extremely pronounced regarding attacks by stray cats. The number of calls regarding bites from wild animals, namely squirrels and wild and synanthropic rodents, has increased significantly.
Conclusions: In order to reduce the frequency of dangerous contacts with wild animals, in particular with squirrels, as well as with pets, it is necessary to carry out sanitary educational work with the population, especially children. The issue of installing warning boards in parks with a ban on hand-feeding squirrels, and installing feeding tables and feeders should be considered.
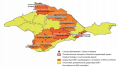
Objective: to evaluate epizootic monitoring of tularemia in the Donetsk region.
Materials and methods: methods of retrospective, statistical, and comparative analysis were used. The sources of infection were investigated using serological and biological methods. The data of industry statistical reporting on form No. 40-annual of the department of especially dangerous infections of the Donetsk regional Sanitary and Epidemiological Station (since 2013 — SSESU, since 2015 — Republican Center for Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Service of the Ministry of Health of the DPR) were used. 20 "Maps of epizootological and epidemiological examination of the focus of zoonotic disease" (F.391/y) were studied.
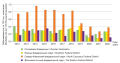
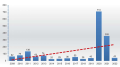
Results: since 1987, the number of enzootic territories in the Donetsk region has increased annually: from 2 settlements in 1987 to 79 (in 4 cities and 16 districts) in 2023. With the beginning of active hostilities, the epidemic process of tularemia in Donbass has sharply intensified. Antibody titers (1:80 and 1:160) for tularemia were detected in environmental samples: in the North Steppe zone — 6.2%, Donetsk-Kryazhnaya — 10.4%, Primorsko-steppe — 15.8%. In the study of mouse-like rodents, 6 cultures of Francisella tularensis holarctica biovar II era R were isolated, resistance of the strain to ampicillin, cefotaxime, erythromycin, clindamycin, polymyxin was established; sensitivity to gentamicin, fluoroquinolones, rifampicin, doxycycline, levomycetin.
Conclusions: the activation of epizootic processes of tularemia in the DPR is associated with the conduct of hostilities. High titers of antibodies to tularemia in environmental samples are noted in the south of the Donetsk region.
Objective: analysis of epizootiological and epidemiological aspects of natural focal infections, namely plague, tularemia, HFRS, West Nile fever, Crimean hemorrhagic fever, Ixodic tick-borne borreliosis, Cu fever, leptospirosis and rabies, in the Volgograd region over 10 months in 2023.
Materials and methods: the article analyzes the epidemiological manifestations of natural focal infections (NFI) in the Volgograd region for 10 months of 2023. The work uses official statistical data from institutions of Rospotrebnadzor of the Volgograd region on NFI for 2023. The main research method is epidemiological analysis.
Results: the numbers of small mammals, potential carriers of NFI, on the territory of the Volgograd region in the 2023 season were within the same indicators of the previous year (SIPY), while the number of ticks in the spring-summer period was higher than the SIPY, but in the fall the number of arthropods in stationary points was lower than in previous seasons. The number of mosquitoes carrying arbovirus infections exceeded the long-term average. When studying environmental objects for the presence of markers of NFI pathogens, a slight decrease in the proportion of positive samples was noted compared to SIPY for all nosological forms. Over the 10 months of this year, there has been a deterioration in the epidemiological situation in the Volgograd region for several infections compared to the same period in 2022. There were 18 cases of West Nile fever (WNF), 10 cases of ixodid tick-borne borreliosis (ITB), and 6 cases of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS). No patients with plague, tularemia, rabies, leptospirosis, Crimean hemorrhagic fever (CHF) and Q fever were identified.
Conclusion: the presence of natural foci of dangerous infectious diseases of varying degrees of activity on the territory of the Volgograd region requires constant monitoring and an adequate response to changes in the foci in order to prevent complications of the epidemiological situation due to NFI.
Objective: to study the intensity of contact with the causative agent of West Nile fever (WNF) of the population of certain central and southern territories of Russia.
Materials and methods: the screening survey covered 1,230 people in 11 regions of the Russian Federation. The work used molecular genetic, immunological and statistical methods.
Results: WNVmarkers, indicating an acute infectious process, were detected in 1.4% of samples. For the first time, local cases of the disease were confirmed in 9 regions of central Russia and the North Caucasus. The circulation of West Nile virus genotype 1 in the territory of the Republics of Ingushetia and Mordovia, genotype 2 in the Ivanovo and Nizhny Novgorod regions, Chuvash and Kabardino- Balkarian Republics is shown. The results of studying the immune layer revealed the presence of antibodies to the West Nile virus of the IgG class in 4.5% of the examined local population, with the highest rates in the Chechen Republic (10%) and the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania (14%). The maximum level of population immunity was noted among people in the age groups 20–29 years old and amounted to 9.7%, 30–39 years old – 7.8%.
Conclusion: the results obtained significantly supplemented our understanding of the spread of WNV in Russia and the activity of disease foci, and can be used in planning and conducting monitoring studies.
OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Recurrent pregnancy loss is not only a medical, but also a social problem of a multifactorial nature. This problem remains unsolvable despite the constant search and application of new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. The presented review examines the literature data on evidence-based methods for diagnosing the causes of miscarriage, as well as methods whose use remains controversial. Special attention is paid to the immunological foundations of a normal pregnancy formation, the violation of which creates the prerequisites for a recurrent miscarriage. The paper also analyzes current data on the role of endometrial receptivity and the contribution of the male factor to the problem of miscarriage, and presents prospects for further research on the problem of recurrent pregnancy loss.
A small, unilateral tumor. Most ovarian leiomyomas (OLM) are benign, but can range from benign to borderline with malignant degeneration. In many patients, OLM are asymptomatic and are detected accidentally during surgery. In rare cases, OLM can be accompanied by severe symptoms as their size increases. This situation requires differentiation these formations from malignant ovarian tumors, which is more often observed during the perimenopausal and menopausal periods. Being discussed that the source of OLM is smooth muscle blood vessel cells, so more undiagnosed small asymptomatic OLMs can be expected. This article presents a clinical case of OLM in a 39-year-old woman operated for uterine myoma. In the case we presented the coexistence of uterine fibroids and ovarian leiomyoma, which subsequently received diagnostic confirmation.
Objective: to increase the effectiveness of in vitro fertilization in patients of late reproductive age by optimizing prepregnancy preparation for the IVF program.
Materials and methods: The study included 67 patients of late reproductive age with a history of unsuccessful IVF attempts, divided into two groups at the second stage of the study, depending on the volume of prepregnancy preparation: group 1 (33 patients), group 2 (34 patients). The control group (50 patients) were healthy women of reproductive age. Immunohistochemical examination of the endometrium and microbiological examination of the uterine cavity, hormonal status of peripheral blood, study of the concentration of melatonin in peripheral blood and follicular fluid, antioxidant status of follicular fluid, expression of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) in the cervical secretion were performed.
Results: in patients with age-related dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis and impaired fertile function, a systemic and local (in follicles) decrease in melatonin levels was revealed. The studied effects of melatonin suggested that its use in patients of late reproductive age with reduced follicular reserve and a "poor" response to ovarian stimulation may increase the effectiveness of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Conclusions: The inclusion in the pre-gravidar preparation of a complex of water-soluble polypeptide fractions of the epiphysis, stimulating the production of endogenous melatonin, made it possible to increase the effectiveness of IVF in patients by an average of 3.1 times according to the criterion of "clinical pregnancy" and 4.1 times according to the criterion of "live birth".
SURGERY
Objective: development, clinical application of a new original method of hernioplasty of median postoperative ventral hernias and biomechanical experimental substantiation of the effectiveness of this method.
Materials and methods: the method of hernioplasty of median postoperative ventral hernias with strengthening of fascial-aponeurotic structures of the anterior abdominal wall was developed and clinically tested on 63 patients. An anatomical experiment was performed in which the biomechanical parameters of the reinforced scar-altered structures of the median parts of the anterior abdominal wall were studied according to the method developed by us.
Results: an increase in the biomechanical parameters of the median structures reinforced by the original method with a frame thread was found: the strength limit of the fascia — by 59.4%, and the modulus of elasticity — by 40.2%, compared with the scar-altered fascia in herniators. These results suggest a confident prevention of recurrence of herniation when using this technique. This assumption was confirmed after the introduction of the technique into clinical practice. In all 63 observed patients, there is no recurrence of herniation for 1-5 years. There were no significant complications of the course of the early postoperative period associated with the applied method of plastic surgery. The method is characterized by material and financial accessibility, the absence of complex technical manipulations that increase the duration of hernioplasty.
Conclusions: the effectiveness in preventing recurrence of herniation, accessibility and simplicity of the proposed method of surgical treatment of postoperative and recurrent ventral hernias allows us to recommend it for wide clinical use.
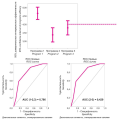
Objective: To compare the long-term results of LSG and RYGB with a fixed restrictive component in patients with morbid obesity in terms of weight loss, control of associated diseases and the development of long-term complications, including sarcopenia.
Materials and methods: our study included the results of treatment of 251 patients (153 LSG and 98 RYGB). The follow-up period was at least 24 months (median follow-up 38 months). The restrictive component was assessed 12 months after surgery using CT-volumetry. The size of the gastroenetroanastomosis was additionally measured using fibrogastroscopy in the RYGB group. The bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) was used to assess body composition and determine the skeletal muscle mass index (SMMI) initially and during control examinations in the postoperative period.
Results: both groups obtained good results in terms of weight loss and control of associated diseases, however, RYGB shows some advantages in these parameters. On the other hand, in the RYGB group a higher rate of progression of signs of sarcopenia was detected (8.2% (including 3% of severe sarcopenia) vs 3.3% in the LSG group). Most patients who progressed to sarcopenia were older, had type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), or had mild sarcopenia at baseline.
Conclusions: RYGB demonstrates better results in terms of weight loss and control of associated diseases compared to LSG, however, in elderly patients, as well as in the presence of T2DM or signs of sarcopenia, it is advisable to choose operations without a pronounced malabsorptive effect.
INTERNAL DISEASES
The subject of medical science is human health. Health is a property of the body. This can only be understood within the framework of a theoretical model. To date, such models do not exist; one of the attempts to create it was the theory of functional systems by P.K. Anokhin, however, it was not completed. At the same time, there are no theoretical models of simpler organisms than humans. Moreover, there is no methodology for creating such models. Empirical approaches implemented in private medical sciences, such as physiology, anatomy, cytology, etc., can in no way become the basis for the formation of a theoretical model of the body, without which understanding health is impossible. This article proposes a framework for developing a model of the human body.
Objective: to evaluate the possibility of using artificial neural networks for integration into the medical decision support system as an optimization of outpatient management of patients with COPD.
Materials and methods: a dynamic followup of 150 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, registered at the dispensary for the underlying disease, who completed the outpatient stage of pulmonary rehabilitation after a moderate exacerbation was carried out. The material of the study was a universal questionnaire of 69 indicators, including anamnesis, clinic, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics. A four-layer neural network has been created: the first two layers — 69 neurons, the third layer — 34 neurons and the last layer — 3 neurons.
Results: the software was used in the Java programming language using the Encog 3.4 module.
Conclusion: the use of the capabilities of artificial neural networks for integration into the medical decision support system in the outpatient management of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease has shown high specificity. The predictive model is implemented in the form of a computer program: "The program for predicting an unfavorable outcome, the development of cardiovascular complications and the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (CardioRisk)" and was introduced into the work of outpatient polyclinic institutions in Rostov-on-Don.
CARDIOLOGY
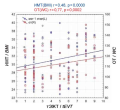
Objective: to assess the thickness of epicardial adipose tissue in patients of different BMI, to establish relationships with the lipid profile during 48 months of observation.
Materials and methods: 121 men were selected for an open prospective study. Three main groups were identified: group 1 — 24 patients with normal BMI (20%), group 2 — 35 men with excess BMI (29%), group 3 — 62 obese patients (51%). The control group (4) included 27 practically healthy men. Three stages of prospective observation of patients were determined: at the time of hospitalization, 12 and 48 months (±2 weeks) from the index event.
Results: EAT thickness measured by echocardiography in patients with STEMI correlated with BMI, waist circumference (WC) throughout of the entire study, the strength of the connection was significantly higher with OT. EAT thickness in patients with STEMI increased in the over-BMI and obesity groups from the beginning to the end of the study (p <0.05) and was statistically significantly higher than in the control group and in patients with normal BMI. Throughout the study, eVT had a weak positive correlation with the level of blood triglycerides, total cholesterol and LDL-C.
Conclusions: the thickness of epicardial adipose tissue correlates with waist circumference and atherogenic indicators of lipid metabolism.
INTERNAL DISEASES, ALLERGOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Objective: to evaluate the dynamics of the T- and B-cell immunity in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who have and have not had COVID-19, depending on the number of CD3+CD8+T-lymphocytes.
Materials and methods: 65 men with ACS who underwent coronary artery stenting were examined. Immunological parameters were studied using flow cytometry, a complete blood count at baseline and 28 days after admission.
Results: The maximum troponin level was observed in individuals with ACS who had recovered from COVID-19 and had a normal level of CD3+CD8+T cells. Stent thromboses and deaths occurred only among patients with a history of COVID-19, mainly with reduced CD3+CD8+T-cells, for which indicators of immune status were determined over time. The absolute numbers of T lymphocytes, T helper cells, late activated T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes (CD3-CD19+CD5+), B lymphocytes (CD45+CD3-CD19+) were minimal in individuals with low CD3+CD8+ T lymphocytes who had previously suffered from COVID-19, and significantly increased in their dynamics after 28 days. Natural killer cells significantly increased in dynamics in patients with initially low and normal CD3+CD8+T-lymphocytes who suffered from COVID-19.
Conclusions: after stenting of the coronary arteries over time, in people with reduced CD3+CD8+Tlymphocytes and patients with COVID-19, T-lymphocytes (CD45+CD3+CD19-), T-helper cells, CD3+CD8+T-lymphocytes significantly increased, T-NK lymphocytes, NK lymphocytes, late-activated T-lymphocytes, T-regulatory lymphocytes and late-activated T-regulatory cells, B-lymphocytes, immunoglobulin G and complement fragment C3a decreased. T-regulatory lymphocytes and late-activated T-regulatory cells were significantly reduced in patients without prior COVID-19 with baseline low CD3+CD8+T-lymphocytes. In individuals with normal CD3+CD8+T-lymphocytes who recovered from COVID-19, T-lymphocytes (CD45+CD3+CD19-), NK-lymphocytes, and late-activated T-lymphocytes increased over time.
PEDIATRICS, ALLERGOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Objective: to study the features of the clinical picture and the innate immune response in children with various variants of the course of acute urticaria.
Materials and methods: 236 children with acute urticaria were examined. Clinical research methods included an analysis of the medical history of life and disease, an objective examination of the child, immunological research methods consisted in determining the content of lactoferrin, IL-4, IL-6, IL-17, IFN-γ, TGF-β, the active form of VEGF-A by enzyme immunoassay of blood serum.
Results: clinical and anamnestic data of various variants of the course of acute urticaria in children, depending on the values of UAS7, revealed the features of the course of the disease in childhood; in some patients, severe acute urticaria was an integral part of anaphylaxis of various origins; cytokine spectrum analysis records hyperproduction of IFNy in children with acute urticaria, regardless of the severity of its course, a decrease in IL levels-4 in the blood serum of children with all variants of acute urticaria, increased concentration of lactoferrin, IL-6, IL-17, significant hyperproduction of TGF-β, the active form of VEGF-A in severe acute urticaria.
Conclusion: the revealed changes indicate an imbalance in the functioning of the innate link of the immune system, activation of the cytokine cascade of inflammation, which leads to the launch of regulatory mechanisms of the inflammatory process, while in childhood there is a clear dependence of the severity of the imbalance of the immune response and the severity of acute urticarial.
ALLERGOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Objective: In a prospective cohort study to evaluate the clinical and immunological efficacy of differentiated targeted interferon and immunomodulatory therapies focused on identified pathological immunophenotropes and associated clinical manifestations in immunocompromised patients suffering from atypical chronic active herpes viral infections (ACA-HVI).
Materials and methods: 335 patients suffering from mixed-AHA-HVI were examined. The study complex included: methods for detecting herpesviruses: serodiagnosis, PCR-RV; immunological methods: a research of subpopulation of blood lymphocytes (method of a flow cytometry), determination of the spontaneous and induced products of IFNα and IFNγ, levels of serum cytokines and immunoglobulins (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, TNFα and IFNα and IFNγ, Ig A, M, G) by ELISA. The study was approved by the ethics board and informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Results: Integral formulas of disorders in the antiviral immune defense system were created, which made it possible to isolate 3 pathological immunophenotypes (PIF): PIF1: NG↓+ind.IFNα/IFNγ↓+CTL↓+EKK↓+IgM↑+hypecytokinemiya (IL-1β↑+IL-6↑+TNFα↑); PIF2: NG↓+ ind. IFNα/IFNγ↓ + EKK↓+ IgG↓+hypercytokinemiya (IL-1β↑+IL-6↑+TNFα↑) and PIF3: NG↓+ind.IFNα/IFNγ↓+hypercytokinemiya (IL-1β↑+IL- 6↑+TNFα↑). Taking into account the identified disorders, a program of targeted interferon and immunomodulatory therapy was developed for each PIF: local and systemic IFN therapy + hexapeptide was developed for PIF1; for PIF2- local and systemic IFN therapy + glucosaminimuramyldipeptide; for PIF3-local and systemic IFN therapy.
Conclusions: High clinical efficacy was demonstrated in 100% of patients with three groups of ACA-HVI. Immunological effectiveness of targeted interferon and immunomodulatory therapy programs: 89.5% for PIF1; for PIF2-57.6% and for PIF3- 37.5% of cases.
Статьи
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)