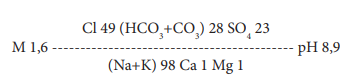OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
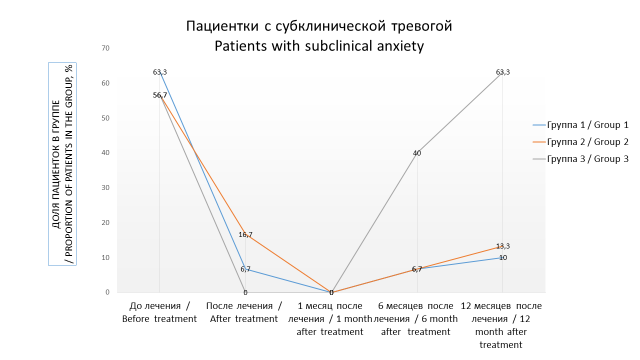
Objective: studying of the effect of combined antioxidant and photodynamic therapy (PDT) on the emotional state of patients with vulvar kraurosis.
Materials and methods: the study involved 90 women with vulvar kraurosis who were randomized into three groups of 30 participants. In the first group, treatment included photodynamic therapy (PDT) followed by administration of the antioxidant Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate for one month. Participants in the second group received only PDT. Patients of the third group underwent a course of laser therapy on the perineal region. The emotional state of the participants was assessed using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) before and at the end of treatment, 1, 6 and 12 months after the end of therapy.
Results: before treatment, participants from the three groups scored a similar number of HADS scores. In the course of observations, the best result on the scales of anxiety and depression was recorded in patients who received combined antioxidant and photodynamic therapy. After a month of taking Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, the HADS score in these women was significantly lower than in the comparison groups. Further, these patients continued to show better scores on the depression scale. The total scores on the anxiety scale in this group were comparable to those in patients who received only PDT.
Conclusion: combined antioxidant and photodynamic therapy, including Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate, has a more pronounced positive effect on the emotional background of patients with vulvar kraurosis in comparison with PDT and laser therapy.
PSYCHIATRY AND NARCOLOGY
The article presents a review of the literature on the subject of non-suicidal self-injurious behavior (NSSI), the study of which attracts the attention of authors, both in the Russian Federation and around the world. Large meta-analyses of NSSP studies, proposed models, probable causes and mechanisms of occurrence, neurobiological factors, social factors, as well as the influence of modern means of communication and social networks are considered.
Objective is to study, summarize and present data on the causes and risk factors of non-suicidal self-injurious behavior. Research method — articles in the “MEDLINE/PubMed”, “Scopus” databases in international medical journals were selected and analyzed. Articles were searched by keywords: “Self-Injurious Behavior”, “Non-Suicidal Self Injury”, “Deliberate Self-Harm”, “Self-Harm”, “Risk Factors”. Inclusion criteria: publication date from 2017 to 2022, clinical studies, meta-analyses and systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, availability of the full text in the public domain or abstract. Exclusion criteria: abstracts; monographs, study guides; publication date until 2017, inconsistency with the research topic. A total of 94 publications were found. The review included 61 publications from 2017 to 2022 that corresponded to the topic and purpose of the study, and also added 19 sources older than 2017 that are significant for disclosing the subject of the study from references in the reference lists of the analyzed sources.
INTERNAL DISEASES
Objective: to study the mechanism of action of low-mineralized sulfate-chloride-sodium mineral water on the clinical picture and motor function of the stomach in patients with epigastric pain syndrome using the regulatory peptide motilin as an example.
Materials and methods: 113 people of both sexes were examined, the average age was 22.3±0.21 years. The observation group (57 people) included individuals with functional dyspepsia in the variant of epigastric pain syndrome, the comparison group included practically healthy individuals (56 people). The questionnaire method was used according to the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale questionnaire; ELISA method for determining the concentration of motilin in the blood. Mineral water in a volume of 200 ml was taken once by both groups of patients, patients with EPS additionally received a course.
Results: in persons with epigastric pain syndrome, abdominal pain prevails. The course intake of mineral water provides a positive clinical trend, confirmed by a decrease in the syndromes of lesions of the upper gastrointestinal tract. A single and course intake of mineral water provides a stable increase in the level of motilin in functional dyspepsia.
Conclusion: patients suffering from functional dyspepsia in the variant of epigastric pain syndrome have persistent disorders of motilin secretion compared with healthy individuals. Stimulation of the stomach on a drinking test model showed inadequacy of changes in the level of this hormone. Both a single and a course intake of low-mineralized sulfate-chloride-sodium mineral water contributes to an increase in the concentration of motilin, which should be considered as a physical adaptogenic factor leading to a stable ordering of the body’s functional relationships.
Very few works are devoted to the problem of medical semiotics, meanwhile, modern medical science, having received new research methods, expanding knowledge about diseases and the human body, continuously introduces new concepts, terms, indicators. Their integration into the general context of medical semiotics is an important problem. A significant difficulty is the large volume of symptoms, syndromes currently accumulated in medicine. This article is devoted to the transformation of empirical medical semiotics into analytical one. The authors, relying on the apparatus of theoretical semiotics, proposed a new classification of symptoms and the concept of the meaning of symptoms. These approaches make it possible to make all the array of medical symptoms available for use by a doctor and to diagnose diseases based on a logically consistent and modeling human thinking algorithm. The article outlines a further program for the improvement and development of medical semiotics.
ENDOCRYNOLOGY
Disorder of sex development (DSD) is a term used to refer to congenital disorders that led to atypical structure of the genitals. The cause of DSD is a disorder of the embryonic development of the reproductive system due to chromosomal, genetic pathology or other adverse effects on pregnancy. DSD entails difficulties with social adaptation of the family, leads to severe psychological disorders in the child and his relatives. Sex of a child with DSD should be established only after a full examination and consultation of specialists in this field. A clinical case is presented to illustrate the complexity of differential diagnosis and choice of passport sex in a child with one of the rare forms of DSD.
PAEDIATRICS
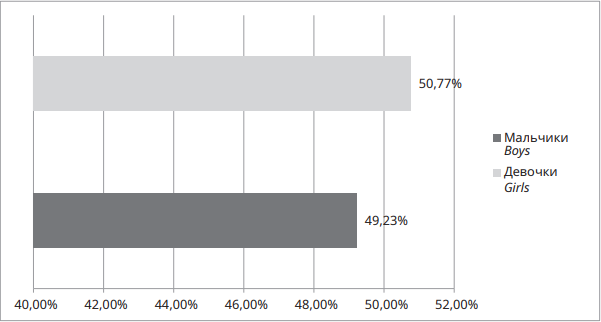
Objective: to determine the feasibility of using INTERGROWTH-21st centile tables in assessing the physical development of full-term newborns in the Republic of Crimea.
Materials and methods: a retrospective analysis of 1300 birth histories of full-term newborns whose mothers permanently reside on the territory of the Republic of Crimea was carried out. Mass and length, chest and chest circumference were analyzed. The assessment of the obtained anthropometric indicators was carried out by the centile method according to the INTERGROWTH-21st tables. In the study, we conducted a comparative assessment using the accepted INTERGROWTH-21st standards, comparing them with the accepted domestic assessments of the state of the physical development of newborns.
Results: the values of anthropometric indicators of boys in the Republic of Crimea are shifted towards higher estimates. Estimates “below average”, “low”, “very low” are found in no more than 3% of cases. “Above average”, “high”, “very high” are much more common: with 10% — for weight/length ratio, 18% — for weight, 34% — for length, and 51% — for head circumference. The values of anthropometric indicators of girls in the Republic of Crimea are also biased towards higher estimates. Ratings of “below average”, “low”, “very low” are very rare: 6% — for the weight/length ratio, 4% — for the weight rating, less than 1% — for the body length rating and 2% — for the head circumference. “Above average”, “high”, “very high” scores are much more common: 8% — for weight/length ratio, 15% — for weight score, 45% — for length score, and 30%— for OH.
Conclusions: we consider the use of centile tables INTERGROWTH-21st in assessing the physical development of full-term newborns of the Republic of Kazakhstan to be inappropriate and we see the need to develop regional standards.
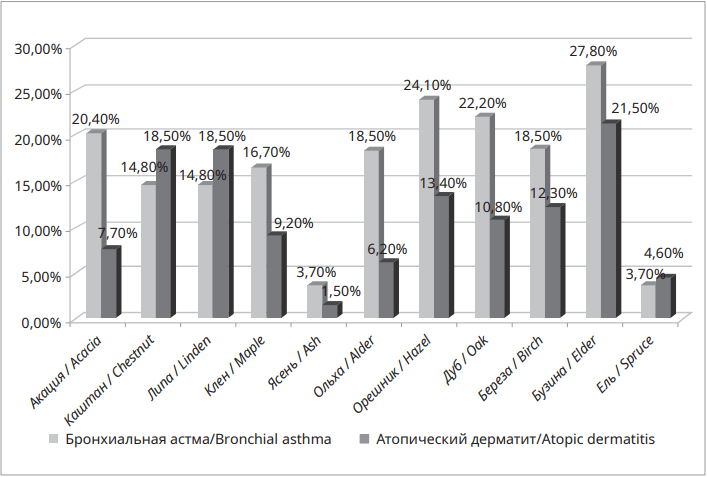
Objective: to investigate the characteristics of pollen sensitization in children with established diagnoses of bronchial asthma (BA) and atopic dermatitis (AD) living in the Rostov region.
Materials and methods: patients suffering from BA (n = 53), they made up the first group and patients with AD (n = 65), the second group were examined. All children underwent a comprehensive clinical and laboratory examination. Immunochemiluminescent assay by the Immulight 2000XPi analyzer was used to determine specific IgE.
Results: the analysis of the obtained results showed that sensitization to tree pollen was quite often noted - at least a quarter of those examined with BA and about 20% of children with AD had elevated titers of specific IgE to these allergens. The study of the level of specific IgE to meadow grass pollen showed that in the first group an allergic reaction to pollen of bent grass (31.5%), bonfire (33.3%), timothy grass (29.6%) and fescue (28.3%) was noted more often. In the second group, elevated levels of specific IgE were registered in relation to grasses such as bent grass (31.80%), bonfire (27.7%) and timothy grass (21.5%). The highest level of sensitization in patients with respiratory manifestations of allergy was registered in relation to weed pollen: ragweed (40.7%), quinoa (22.2%) and chamomile (14.8%).
Conclusion: this study made it possible to identify allergens that play the most important role in the pathogenesis of BA and AD in children living in the Rostov region.
A clinical case of a familial form of peroxisomal D-bifunctional protein (DBP) deficiency (OMIM 261515) with an unfavorable (fatal) outcome caused by a mutation in type 4 17ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD17B4) with a nucleotide replacement of chr5:118788316G>A in the homozygous state is presented. (D-bifunctional protein deficiency or 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase IV deficiency). Bifunctional protein deficiency is an autosomal recessive birth defect of peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation. The total incidence of morbidity is one case per 50,000 newborns. Most peroxisomal disorders manifest in the early neonatal period with an extremely severe course and phenotypic features, which facilitates their diagnosis. This is the difference between them and diseases with a milder and prolonged course, which debuted at different age periods, often had no neonatal or infantile symptoms and were accompanied, in some cases, by satisfactory cognitive functions. The purpose of the report was to highlight the clinical manifestations, variants of the course and complexity of the diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders to a wide range of doctors of different specialization: in the field of perinatology, pediatrics, neurology, genetics, endocrinology.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Acinetobacter baumannii is a gram–negative, aerobic, oxidase-negative microorganism, a pathogen that causes serious nosocomial infections, as well as community-acquired pneumonia, especially in people with weakened immunity and multiple organ diseases, all over the world. A. baumannii survives for a long time on various surfaces, medical equipment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), this microorganism is classified as a threat to human health. The review describes the main factors of pathogenicity of A. baumannii: outer membrane proteins, pili, LPS, capsule, siderophores, biofilm formation, secretion systems. The literature search was carried out using databases “Scopus”, “Web of Science”, “RSCI”, “MedLine”, in the period from 1992 to 2022. The selection of literature sources was carried out based on the availability of information on the study of pathogenicity factors of Acinetobacter baumannii. 60 literature sources were selected that meet the necessary criteria. The search was carried out using keywords and phrases, such as “A. baumannii”, “pathogenicity factors”, “outer membrane proteins”, “pili”, “LPS”, “capsule”, “siderophores”, “biofilm formation”, “secretion systems”. The review presents the latest achievements obtained by foreign and domestic authors. A. baumannii, like other pathogens, requires the coordinated work of various pathogenicity factors for the occurrence of infection. Together, pathogenicity factors enable the microorganism to survive in hospital conditions. Scientific research data indicate a high degree of heterogeneity of A. baumannii strains. Further research should be aimed at molecular genetic studies of the mechanisms of pathogenicity, the emergence of resistance to antimicrobial drugs. Understanding what mechanisms and factors contribute to the virulence of strains is necessary for the development of new methods of combating A. baumannii.
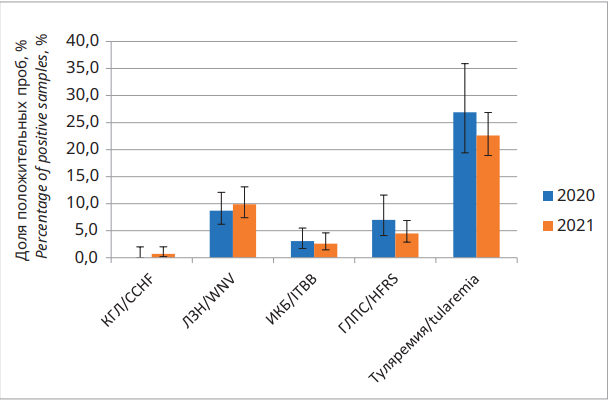
Objective: to analyze the results of blood sera comprehensive study of the local population of the RR, conducted in 2021 to assess the state of natural and zoonotic focus of CHF, WNF, ITBB, tularemia and risk of possible spread of Haemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS).
Materials and methods: 424 blood serums obtained in 2021 from healthy donors living in 10 administrative territories of the Russian Federation were tested by enzyme immunoassay.
Results: in 2021 the detection rates of specific antibodies in the studied areas were: WNF — 9,9 %, HFRS — 4,5 %, ITBB — 2,6 %, CHF — 0,7 %, tularemia — 22,6 %. When comparing the results obtained in 2020 and 2021, the difference in the proportions of seropositive samples is not statistically significant.
Conclusions: the study of the immune layer to NFI in selected population groups confirms the circulation of pathogens in RR territory. The monitoring results demonstrate the extensive, mostly combined nosoareals of NFI of viral and bacterial etiology and the contact of the local population with them.
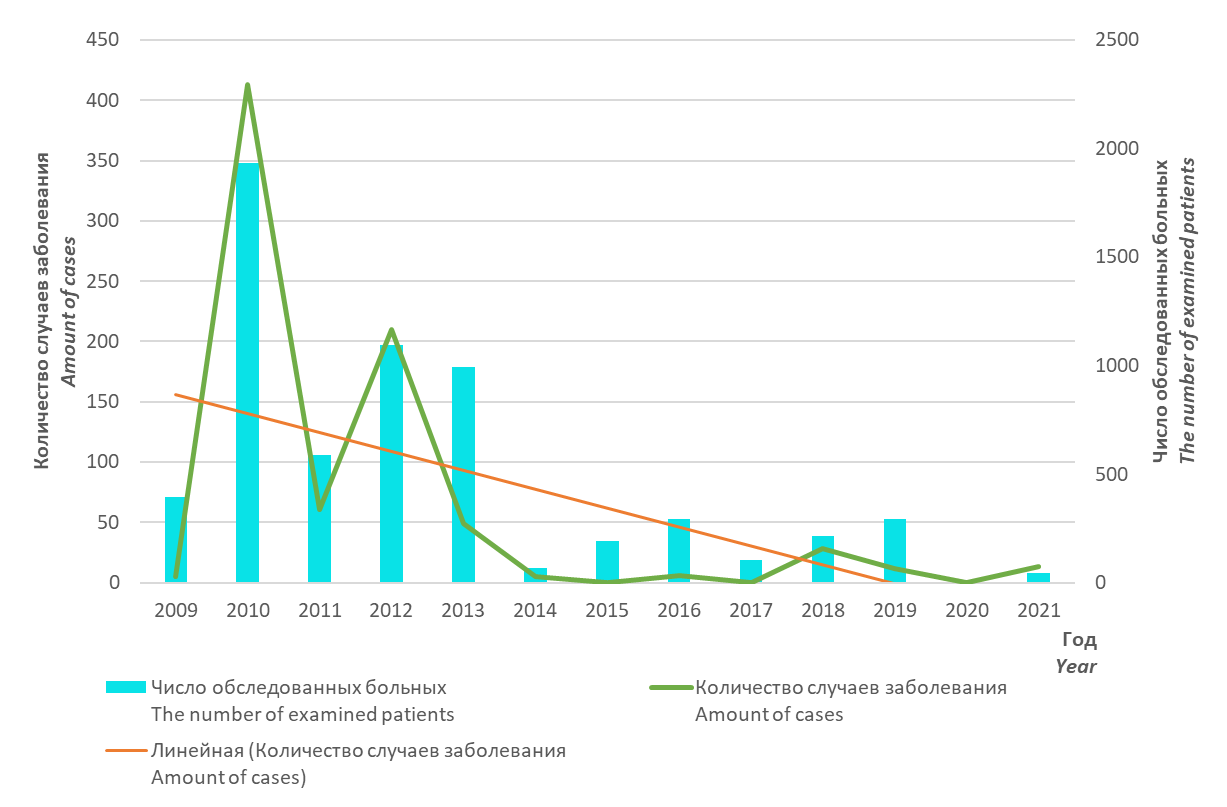
Objective: the study of molecular epidemiological and clinical aspects of EVI in the Rostov region for the period 2006-2020. to improve the disease surveillance system. Research methods: epidemiological, virological, molecular biological (PCR, sequencing, phylogenetic analysis), microbiological, statistical.
Materials and methods: the analysis of medical records of 139 patients with EVI was carried out. Samples of biomaterial (feces, throat swab) from 17293 people, samples from environmental objects (2710 samples), strains of enteroviruses (EV) in the amount of 142 specimens were studied.
Results: in the Rostov region until 2013. sporadic incidence of EVI prevailed with registration from 1 to 38 cases per year. June 2013 there was a sharp increase in the incidence of EVI with the formation of local foci in organized groups, associated with the circulation of a new genotype — EV 71 type of subgenotype C4 of “Chinese” origin (622 patients with EVI were registered, one death). The clinical features of the disease were determined: acute onset with manifestations of intoxication, foot and mouth disease-like syndromes, followed by the development of CNS pathology in 37.4% of patients. According to the results of sequencing of biomaterial samples from patients and virus carriers for the period 2006-2020. EVs of 22 types were detected.
Conclusions: EVs are subject to intense genetic variability, due to which new genovariants pathogenic for humans may appear. The change in EV genotypes, which dominated the circulation among the population of the Rostov region, determined the rise in the incidence of EVI in 2013. A significant diversity of non-polio EV genotypes was revealed, while the structure of EV genovariants changed in different years.
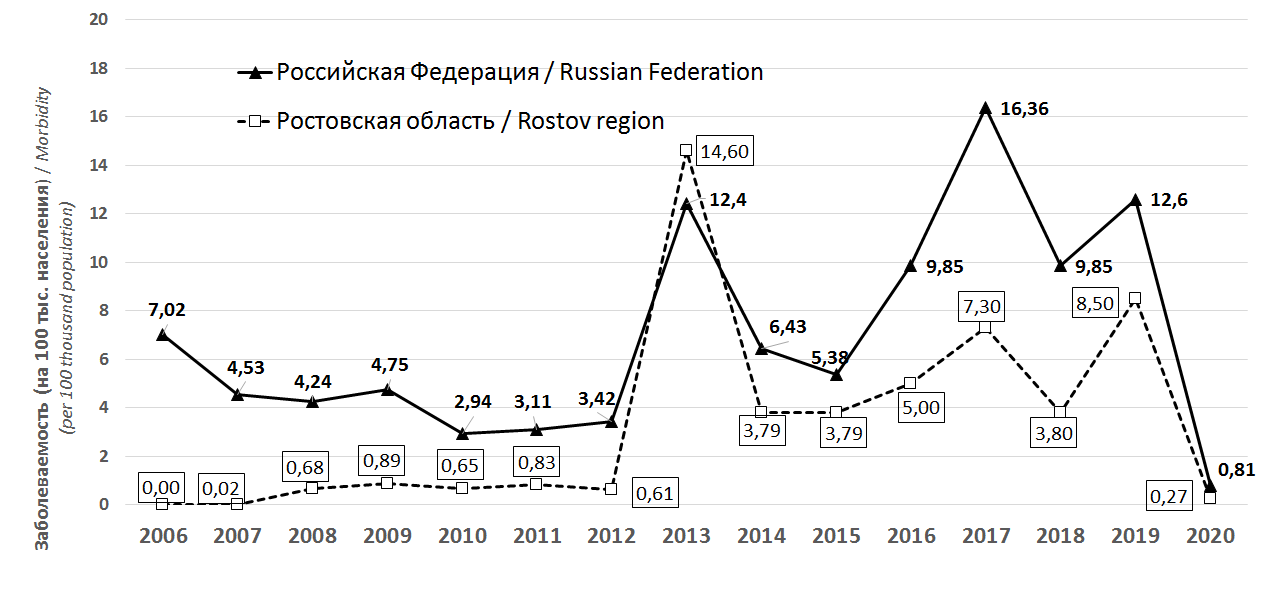
Objective: to assess the quality and effectiveness of West Nile fever (WNF) causative agent’s monitoring in the Volgograd region and to develop a set of measures to its optimization.
Materials and methods: data on the detection of WNV cases, results of serological and zooentomological monitoring in 2009–2021. A comprehensive methodological approach was applied, including statistical and epidemiological methods.
Results: based on the assessment of WNF causative agent’s monitoring key aspects in the Volgograd region, it was shown that one of the priority problems is the insufficient and untimely detection of cases among the population. Among the urgent problems of serological monitoring are the lack of a clearly established frequency of serological examination in the population of the region’s administrative territories and the termination of one of the indicator population groups examination, regulated by the current regulatory and methodological documents. An assessment of the parameters of monitoring studies of the external environment indicates an insufficient territorial coverage and a decrease in the volume of studies, primarily in relation to the main carriers of the West Nile virus, which determines the overall low detection rate of West Nile virus markers.
Conclusion: recommendations are proposed for optimizing monitoring, which will enhance the efficiency of WNF epidemiological surveillance and develop a scientifically based forecast of the development of the epidemiological situation.
OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE
The article describes the current issues in occupational medicine and the ways to resolve them in the context of the spread of a new coronavirus infection COVID-19. The risks of COVID-19 infection in medical and non-medical workers are considered. Modern approaches to establishment of COVID-19 causal relationship with occupation and medical examinations in patients with COVID-19 are presented. The main provisions of the National concept of healthcare-associated infections relevant in the context of COVID-19 pandemic are presented. Problems in public health care related to restructuring of work of medical organizations in conditions of COVID-19 spread are shown. Attention is paid to mental health disorders in medical workers providing medical care to patients with COVID-19. The prospects of development and implementation of measures for prevention of COVID-19, its complications and adverse outcomes taking into account complex assessment of working environment and professional health of workers are considered from the position of occupational medicine.
Objective: based on a comprehensive assessment of the levels of anxiety and burnout syndrome among medical workers of COVID hospitals, develop measures to prevent mental health disorders.
Materials and methods: examined: group 1 — medical workers of COVID hospitals (n=201); group 2 — medical workers of multidisciplinary hospitals (n=195); group 3 — medical workers of the outpatient clinic link (n=186). Control group (n=190) — employees of engineering, technical and economic specialties (healthy). Methods: psychological (“integrative anxiety test”, authors: A.P. Bizyuk, L.I. Wasserman, B.V. Iovlev (2005); method for diagnosing professional burnout according to V.V. Boyko). During statistical processing, the significance of differences was determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by intergroup comparisons according to Dunnet’s test. The obtained data were processed using the statistical package “Statistica” from StatSoft (USA).
Results: in the study of the phases of emotional burnout, it was revealed that medical workers in COVID hospitals had significantly higher scores of the phase of stress, phases of resistance compared to medical workers in multidisciplinary hospitals and outpatient services. At the same time, the total score of the exhaustion phase was significantly increased in medical workers in COVID hospitals compared to medical workers in multidisciplinary hospitals, but there were no significant differences in this indicator when compared with medical workers in outpatient services. It has been established that among medical workers of COVID hospitals, the indicator “alarming assessment of prospects” prevails; in medical workers of multidisciplinary hospitals — “asthenic component”; among medical workers of the outpatient clinic link — a «phobic component».
Conclusions: among medical workers of COVID hospitals, there is a high level of formation of phases of emotional burnout and anxiety. Measures to prevent mental health disorders of medical workers in COVID hospitals include: socio-psychological, professional and organizational.
ALLERGOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by M. leprae with a primary lesion of the skin and peripheral nervous system. Currently, clinicians using bacterioscopic studies of scarification and skin biopsy mainly diagnose leprosy. However, the development and application of new diagnostic criteria, especially those associated with damage to nerve fibers, remains an urgent task of modern leprology. This review considers the important role of neurotrophic factor (nerve growth factor, NGF) in the pathogenesis of nervous system damage in leprosy and establishes the relationship between NGF levels and forms of the disease. The review includes data from foreign and domestic articles; the search was carried out using the “Scopus”, “PubMed”, “Web of Science”, “elIBRARY” databases.
Objective: to assess changes in the immune status before and after coronary bypass surgery.
Materials and methods: included 70 male patients with coronary atherosclerosis (group 1) and 30 volunteers (group 2) without signs of coronary artery disease comparable in age to group 1. Immunity parameters were studied before surgery, after 4–5, 9–10 and 28–30 days by the method of phenotyping of CD3+ populations; CD3+CD4+; CD3+CD8+; CD3+CD25+; CD3+CD45+; CD3+CD95+; CD4+CD25+; CD4+CD154+; CD19+, CD19+CD40+. The levels of Ig A, M, G were assessed by the method of radial immunodiffusion in the gel. Serum precipitation in polyethylene glycol was used to determine circulating immune complexes. Statistical analysis of the study results was performed using the Statistica 12.0 program (StatSoft, USA). Statistical significance was considered significant at p<0.05.
Results: in patients of the IHD group, uncoupling of the processes of T-lymphocyte activation, their maturation and apoptosis was noted; suppression of immunoregulation and activation of intercellular cooperation. After CABG, in dynamics, these processes reflect the multidirectional changes.
Conclusions: in patients with coronary atherosclerosis, there is a discoordination of the processes of T-lymphocyte activation, their maturation and apoptosis. Suppression of immunoregulation and activation of intercellular cooperation. In the dynamics after CABG, immunity parameters differ in different directions in different periods of observation and demonstrate different degrees of involvement of adaptive mechanisms of immune defense.
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)