OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
Objective: to evaluate the results of surgical correction of pelvic organ prolapse using mesh implants.
Materials and methods: experience in the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse using mesh implants on the basis of the Federal Siberian Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia is presented. The features of the surgical technique for performing laparoscopic sacropexy and pectopexy, the advantages and disadvantages of both techniques, as well as the results obtained after surgery are considered.
Results: during the period from 2016 to 2022, 567 surgical interventions using mesh implants were performed at the gynecology department. The effectiveness of POP correction using laparoscopic access reached 93.4% (p< 0.001). The recurrence rate of apical prolapse was 6.6% (p< 0.001). 20% of patients experienced constipation after sacropexy (p< 0.001), which was not observed after pectopexy. The prevalence of stress urinary incontinence de novo after laparoscopic sacropexy was 4.1%; this complication was not diagnosed after pectopexy. 37.4% of patients who underwent laparoscopic sacropexy reported dyspareunia, whereas 6.1% of women who underwent pectopexy had dyspareunia (p< 0.001). Also, in 0.64% of cases after urethropexy, a complication such as erosion of the vaginal wall was recorded (p< 0.001).
Conclusions: laparoscopic sacropexy and pectopexy are effective methods of surgical correction of pelvic organ prolapse, and pectopexy has a number of advantages compared to sacropexy.
Endometriosis is a chronic hormone-dependent disease, which is typically characterized by the occurrence of benign growths of tissue, similar in functional properties and structure to the endometrium. This disease affects up to 10% of women of reproductive age, significantly reducing performance, fertility and quality of life. Diagnosis of endometriosis is based on clinical presentation, ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), but diagnosis is often hampered by the lack of objective criteria. Despite the practical necessity, there are currently no minimally invasive, highly sensitive methods for diagnosing endometriosis. The article covers a review of modern literature data on the results of the search for molecular biological markers of endometriosis in ectopic foci and eutopic endometrium, the characteristics of their expression and the possibility of application in medical practice. Works cited in the study were selected using the keywords “endometriosis”, “microRNA”, “molecular markers of endometriosis”, “eutopic endometrium” in the search engines PubMed, MedLine. Publications had to meet the following criteria: published in the last 5–7 years; publication language – Russian, English; access to the full text of the publication; Literature not indexed in medical databases was not examined. Also excluded from the analysis were oncological studies, studies concerning extragenital forms of endometriosis, articles on methods of invasive diagnostics and surgical treatment. As a result, 29 articles were selected that met the selection criteria and maximally reflected the current state of the issue of non-invasive and minimally invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.
PSYCHIATRY AND NARCOLOGY
Objective: to analyze current data on the problem of suicidal behavior of cancer patients.
Materials and methods: the analysis of 49 sources of domestic and foreign authors was carried out. The search was carried out in special medical resources, namely: RusMed, Medline, PubMed, and Web of Science. In addition, electronic libraries such as eLibrary were involved.RU, CyberLeninka and the Library of dissertations and abstracts of Russia dslib.net.
Results: the theoretical analysis of scientific research has shown a significant level of prevalence of suicidal behavior in cancer patients. It should be noted that to date there are no specific scientifically based guidelines for the prevention of suicide and suicidal thoughts among cancer patients.
Conclusion: preventive strategies are proposed, which show the importance of screening suicidal behavior in the general medical network in view of the high incidence of suicides to specialists.
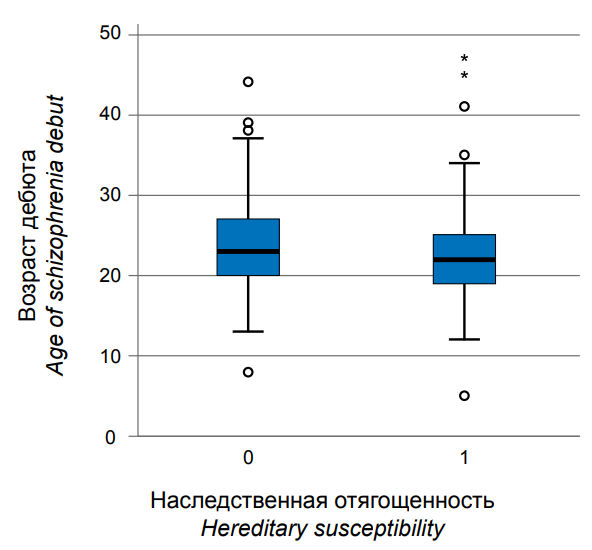
Objective: to identify the characteristics of the clinical debut of schizophrenia, as well as clinical aspects related to hereditary aggravation within schizophrenic spectrum disorders.
Materials and methods: patients with a confirmed diagnosis of F20.0 “Paranoid schizophrenia” selected according to inclusion/non-inclusion criteria participated in the study. Material was collected through clinical interviewing, analysis of medical records and documentation, and self-questionnaires.
Results: a total of 264 individuals participated in the study. Hereditary aggravation with schizophrenic spectrum disorders within two generations was detected in 127 of them (48.1%). Our results showed that having a family history of schizophrenic spectrum disorders correlated with earlier age of schizophrenia debut (p=0.018) and higher scores on the Calgary Depression Scale (p=0.013).
Conclusions: the findings may serve as an effective tool for developing more accurate diagnostic strategies in individuals at high risk of developing schizophrenia due to hereditary aggravation, as well as for the subsequent treatment of these individuals.
INTERNAL DISEASES
Objective: study of indicators of vegetative homeostasis and psychosocial functioning in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) with anxiety-depressive spectrum disorders (RTDS).
Materials and methods: the study involved 112 patients with AS in whom the presence of RTDS was assessed according to the Taylor, Hamilton, Spielberger scales, autonomic disorders by testing according to the methods “Wayne-patient” (VP) and “Wayne-doctor” (BB), heart rate variability (HRV), quality of life (QOL) and clinical and laboratory activity of the disease.
Results: the majority of patients with AS showed signs of RTDS, while this category of patients showed signs of autonomic dysfunction, lower indicators of vital activity, the ability to adapt social functioning and the level of mental health. The HRV indicators obtained in this category of patients indicate an imbalance of sympathetic and parasympathetic influences with the dominance of the sympathetic link of regulation, which confirms the correlation analysis.
Conclusions: patients with AS with RTDS are characterized by low vital activity, reduced adaptation to social functioning, depletion of antioxidant potential. They are characterized by a deterioration in HRV indicators with a predominance of the sympathetic link of the ANS, low resistance to psychoemotional stress with a predominance of the defensive component in the structure of vegetative security.
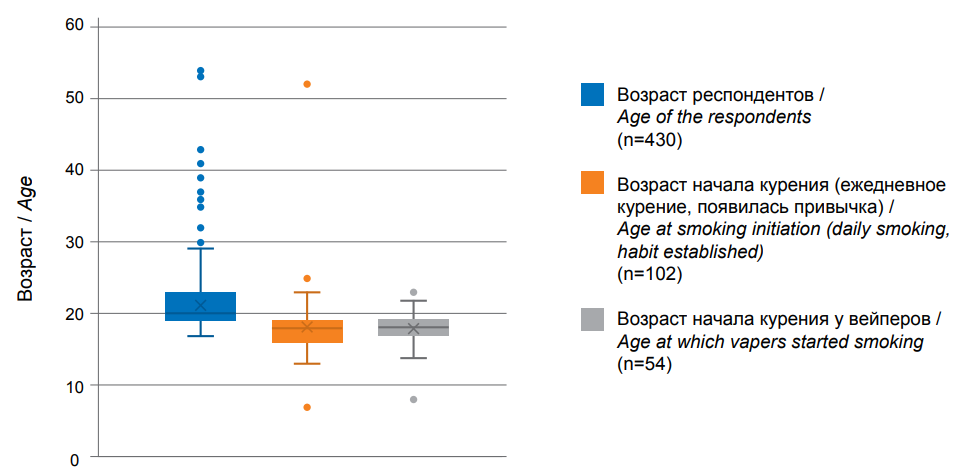
Objective: to study the prevalence of vaping and its negative impact on the health of young people.
Materials and methods: a sociological study was conducted using a voluntary anonymous survey of 430 1st–6th year students of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education “Kaluga State University n. a. K.E. Tsiolkovsky” aged 17 to 54 years.
Results: there were 102 smoking respondents (23.7%) and 328 (76.3%) non-smokers. The average age of smoking initiation was 18.2±0.4 years. The distribution by type of smoking was as follows: vaping with nicotine liquids 46%, regular nicotine cigarettes 28.5%, heated tobacco systems (sticks) 9.8%, vaping with nicotine-free liquids 6.9% and other types of smoking 8.8%. The majority of vapers surveyed, 64.8% (35 people), develop complaints (signs of lung injury associated with vaping) during or after vaping. It was found that significantly more often women noted signs of injury associated with vaping (77.2% versus 22.8% in men, p=0.0036).
Conclusions: the results of the study showed that vaping is the most popular form of smoking among young people, which poses a serious threat to the health of young people.
ENDOCRYNOLOGY
Currently, systemic glucocorticoids are taken by about 1–3% of the general population, up to 1.8% long-term. Moreover, about 50% of patients taking these drugs orally develop glucocorticoid-induced adrenal insufficiency (GIAI) after their withdrawal. Despite this scale of the problem and the length of time the issue has been studied, there are currently no standard algorithms for reducing the dose or discontinuing glucocorticoids. The evidence base on this issue has been performed on relatively few clinical studies, which are extremely heterogeneous with respect to the populations studied, designs, regimens of glucocorticoid use, and diagnostic approaches to adrenal insufficiency. Thus, the weight of evidence on this issue remains inadequate, resulting in each institution having its own approach to dose reduction and discontinuation of glucocorticoids, or no approach at all. This article summarizes current information about GIAI, allowing for improved approaches to dose reduction or discontinuation of glucocorticoids. Improving the management tactics of patients who have been receiving glucocorticoids for a long time will lead to a reduction in the risk of complications of GIAI, including life-threatening ones, as well as to a significant improvement in the quality of life of patients.
CARDIOLOGY
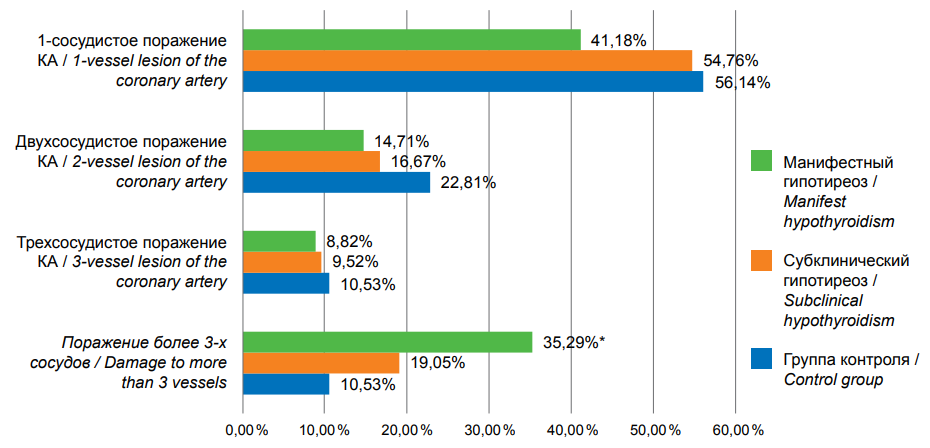
Objective: to assess the incidence of newly diagnosed subclinical and manifest hypothyroidism in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and to identify angiographic features of coronary artery lesions in this combined pathology.
Materials and methods: in all patients with STEMI, the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) was determined, and thyroid function was assessed if the TSH level deviated from the norm. Stage I of the study included 441 patients, stage II included 133 patients with STEMI. Depending on the presence of newly diagnosed hypothyroidism, patients were divided into 3 groups: 1st — patients without hypothyroidism (n = 57), 2A group — with subclinical hypothyroidism (n = 42) and 2B group — with manifest hypothyroidism (n = 34). All patients underwent coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention.
Results: newly diagnosed hypothyroidism occurred in 27.44% of patients with STEMI: subclinical — in 19.73%, manifest — in 7.7% of cases. Patients with concomitant overt hypothyroidism had significantly more severe atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary arteries compared to patients without hypothyroidism.
Conclusion: a high incidence of newly diagnosed hypothyroidism in patients with STEMI was established (27.44% of cases). Multivessel coronary lesions were recorded more often in patients with overt hypothyroidism than in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism and without hypothyroidism.
PAEDIATRICS
A clinical observation of severe combined pathology in a late premature infant with hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system is presented. The extremely unfavorable effect of maternal pathology, in particular diabetes mellitus, on the intrauterine condition of the fetus has been demonstrated, which led to the birth of a premature baby, with the subsequent development of hypoxic-ischemic damage to the central nervous system, intraventricular non-traumatic hemorrhages, diabetic fetopathy, hyperbilirubinemia and the implementation of the infectious process. This case demonstrates that a late premature infant has a combined pathology, which is the basis for using a multidisciplinary approach in their management. Despite the fact that late premature newborns at the time of birth have anthropometric data comparable to full-term ones, they have higher morbidity rates in the early neonatal period. Neonatologists must be wary of this group of children in order to timely determine the scope of the complex of therapeutic measures.
Objective: to study the features of the digestive system in children with reactive asthenic syndrome and correction of disorders using a comprehensive integration program.
Materials and methods: a prospective cohort non-randomized study of 419 children of primary school age was conducted. The main group consists of 128 children living in the territory of active hostilities. Control group — 291 children outside the zone of active hostilities. A full examination was carried out before and 6 months after the start of the comprehensive integration rehabilitation program. All children were collected complaints, anamnesis, analysis of outpatient records, objective examination, examination of the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract.
Results: all children of the main group had complaints from the digestive system. 97 (75.78%) children were concerned about decreased appetite; 79 (61.72%) — stool disorders. Functional disorders were registered in 80 (62.50%) children of the main group, organic pathology — in 62 (48.44%). Among functional abnormalities, functional disorders of the biliary tract were in the first place (in 65 (50.78%) people). Among the organic pathology — diseases of the stomach and 12-duodenum (in 59 (46.09%) children). Peripheral electrogastroenterography revealed in most children of the main group non-impulsive contractions and discoordination of motor skills of varying degrees of severity in all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Conclusions: the implementation of complex rehabilitation measures optimized the studied indicators with more pronounced effectiveness in children evacuated from active combat zones.
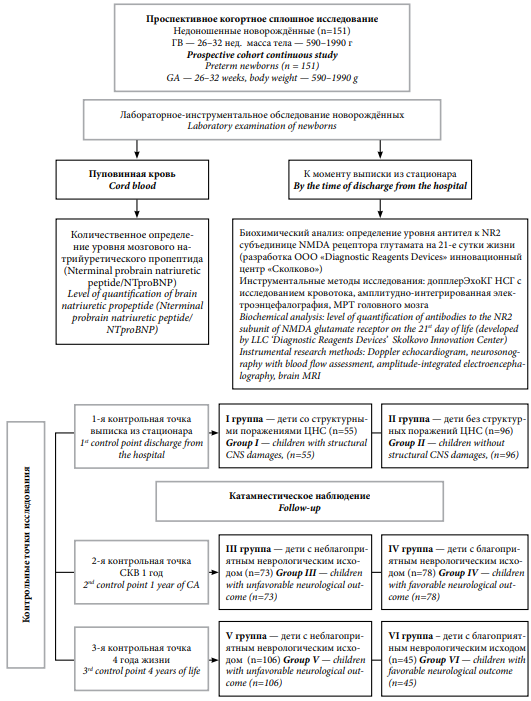
Objective: to assess the prognostic significance of antibodies to the NR2 subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor and brain natriuretic propeptide (NTproBNP) as predictors of unfavorable neurological outcomes in premature children.
Materials and methods: A prospective cohort continuous study included 151 premature children, with a gestational age (GA) of 26–32 weeks and a body weight of 590–1990 gr. The children were measured the quantitation of NTproBNP level in the cord blood and level of antibodies to the NR2 subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor in the blood serum on the 21st day of life. The division of children into groups was carried out in accordance with the assessment of neurological outcomes at control points of the research: 1 control point — at the time of discharge from the hospital, 2 control point — at the age of 1 year of corrected age (CA), 3 control point — 4 years of life.
Results: in the course of the study, it was found a “cascade” increase in the cohort of children with unfavorable neurological outcomes from 36.4% at the time of discharge from the hospital to 70% by the age of 4 years. High values of NT-proBNP level in cord blood and antibodies to the NR2 subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor were established on 21st day of postnatal life in children with both macrostructural brain damages in the neonatal period and having an unfavorable neurological outcome at the age of 1 year of corrected age (CA) and at 4 years of life.
Conclusion: modern neurochemical markers of CNS damages N-proBNP and antibodies to the NR2 subunit of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor open up the possibilities of early diagnosis of brain damages at the cellular level and the start of neuroprotective therapy to reduce neurological disability.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Objective: clinical and laboratory assessment of HIV-infected patients in the intensive care unit with liver cirrhosis that developed as a result of hepatitis of various etiologies.
Materials and methods: a retrospective assessment of 91 medical records of patients with hepatic cirrhosis among 494 HIV-infected patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) was carried out in order to describe the clinical and laboratory features of the course of liver pathology against the background of HIV infection with secondary diseases. The subjects under observation were 46 (50.5%) men, 45 (49.5%) women, median age — 41 years.
Results: patients were diagnosed with profound immunodeficiency (CD4+ lymphocyte count 100,000 copies of HIV RNA per 1 ml — in 45.1% of patients). Child-Pugh class C hepatic cirrhosis was diagnosed in 72.5% of patients. Cirrhosis in most cases developed as a result of toxic hepatitis in combination with chronic hepatitis C (CHC). More than half of the patients showed clinical and laboratory signs of decompensated hepatic cirrhosis. Combinations of two to five secondary infections were diagnosed in 52.8% of patients. The structure of secondary diseases was dominated by bacterial pneumonia, encephalitis and visceral candidiasis. 75.8% of patients did not receive ART, all patients did not receive antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis.
Conclusion: the mortality rate of patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis in the intensive care unit was 80.2% and was associated with the number of secondary diseases and the lack of antiretroviral therapy. Patients with a combination of HIV infection and viral hepatitis require earlier diagnosis and prescription of etiotropic therapy.
ALLERGOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Objective: to identify the frequency and etiology of latent sensitization among frequently ill preschool children living in Rostov-on-Don.
Materials and methods: 40 preschool-age children (5.3±1.2 years old) who are under medical supervision for frequent respiratory diseases of a protracted nature were examined. According to the nature of the clinical course, the following subgroups were identified: 1st subgroup — frequently ill children with recurrent respiratory tract pathology: adenoiditis, bronchoobstructive syndrome (n=19), 2nd subgroup — frequently ill children with different duration of episodes of acute respiratory diseases: from 3 to 5 days and from 5 to 10 days. The mandatory criterion for inclusion in the group was the absence of hereditary burden due to allergic pathology. All patients underwent an allergological examination, including the determination with the help of an automatic immunochemiluminescent analyzer (Immuno CAP 100 Phadia AB, Switzerland) of specific blood IgE to the antigens of Timothy's meadow, rPh1 p1, Phl p 5; antigens of Altenaria alternata, rAlt a1; antigens of ragweed, nAmb a1; to the antigens of wormwood nArt v1.
Results: sensitization to the main allergens that are causally significant for the region is formed in 33–74% of cases in frequently ill preschool children living in Rostov-on-Don. The main causally significant allergen, sensitization to which is diagnosed in most of the subjects, is the major fraction of Ragweed Ragweed (nAmb a1). Sensitization to the major fraction of the common Wormwood allergen (nArt v1) is not diagnosed in a monovariant, but always accompanies hypersensitivity to high Ragweed ragweed.
Conclusions: the presence of concomitant pathology of the respiratory tract in the form of adenoiditis, bronchoobstructive syndrome, as well as a long (more than 5 days) course of frequently recurrent acute respiratory diseases is a factor indicating a high probability of latent sensitization in frequently ill preschool children, which is formed in 33-74% of cases. It is recommended that frequently ill children with symptoms of recurrent respiratory tract pathology perform allergodiagnostics with the identification of specific IgE to the main causally significant allergens for the region.
SURGERY
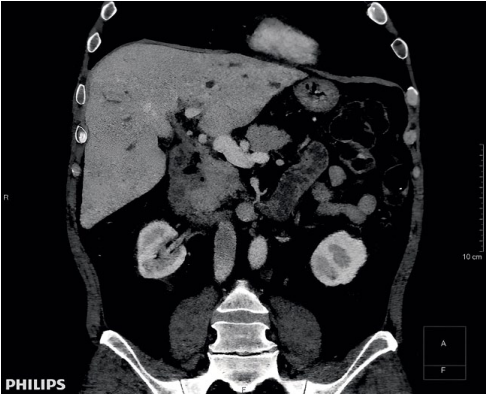
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a disease characterized by inflammation, fibrosis and obliteration of both intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts, accompanied by cholestasis, with further outcome in biliary cirrhosis of the liver, cholangiocarcinoma. The pathogenesis of the disease is poorly understood, but, according to various sources, it involves genetic factors, innate and adaptive immunity mechanisms, the toxic effects of hydrophobic bile acids and, possibly, intestinal dysbiosis. The strong association with inflammatory bowel disease is associated with a significantly increased risk of colorectal cancer, which, along with cholangiocarcinoma, represents the most significant diagnostic challenge in the long-term management of PSC. The diagnosis of PSC is established based on the identification of typical cholangiographic lesions of the bile ducts and the exclusion of secondary causes of sclerosing cholangitis. Complex pathophysiology, heterogeneity of clinical features and the rare nature of the disease have led to the lack of effective therapy to date; there are no treatment algorithms, but a course of ursodeoxycholic acid in doses of 17–23 mg/kg/day can be prescribed for up to a year in order to monitor the dynamics of the decrease in levels serum alkaline phosphatase. A number of drugs are under investigation, including FXR (farnesoid X receptor) agonists with choleretic and antimicrobial properties. Clinically significant stenoses can be successfully treated with interventional endoscopy, but liver transplantation (LT) is currently the only curative treatment with a high survival rate. According to various literature data, 20–25% of patients develop disease relapse in the graft. Our case report of recurrent PSC in a patient 5 years after orthotopic LT provides an overview of management options from a practical, patient-centered perspective.
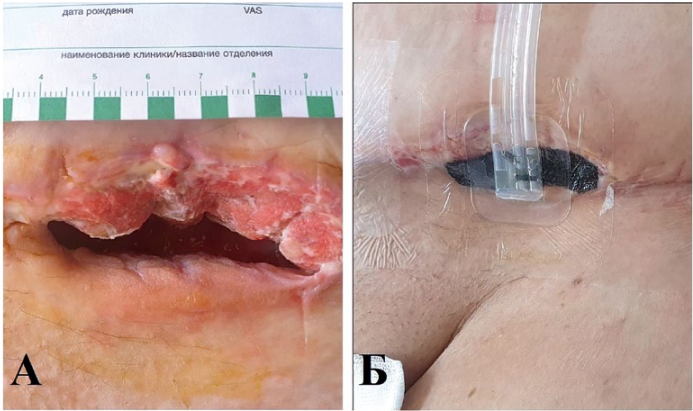
Objective: increase effectiveness of wounds treatment after various etiology by using VAC.
Materials and methods: study included 128 patients with surgical infection. Specter of operations is presented: pilonidal cyst excision — 40 (31.2%), sternomediastinitis — 23 (18%), mesh hernioplasty — 16 (12.5%), laparotomy — 15 (11.7%), emergency laparotomy — 7 (5.5%), traumatology paraimplant complications — 7 (5.5%), abdominoplasty — 7 (5.5%), postoperative esophageal fistulas — 6 (4.7%), decubital ulcers — 4 (3.1%), mammoplasty — 3 (2.3%).
Results: duration of VAC-therapy averaged 22.1±0.26 days. Systemic inflammatory reaction noted in 43 (33.6%) patients. Granulation tissue on 8th day of treatment noted in 98 (76.6%) cases. Microscopically, on day 8 of treatment, inflammatory-regenerative cytograms were detected in 104 (81.3%) patients. Over the course of 16 days, wounds decreased by 62.1±2.5% in all observations. In 47 (36.7%) cases, secondary sutures were applied, in 30 (23.4%) — grafting. A month later, healing was noted in 106 (82.8%) patients. Complications (wound bleeding) were noted in 7 (5.5%) patients. Reoperations were performed in 11 (8.5%) patients. Period of complete healing was 29.3±0.4 days.
Conclusions: vacuum therapy is an effective way to treat wounds in purulent surgery. Time of complete reparative regeneration of wound and period of expensive inpatient treatment are reduced.
PUBLIC HEALTH, ORGANIZATION AND SOCIOLOGY OF HEALTH CARE, MEDICAL AND SOCIAL EXPERTISE
Objective: to conduct a comparative analysis of the previously valid “Card” with a new form of “Card” filled in for patients receiving medical care in a hospital setting with the focus of the attention of practitioners on the new paragraphs of this document.
Materials and methods: a comparative analysis of the medical record of an inpatient patient approved by the order of the Ministry of Health of the USSR dated October 4, 1980 was carried out. No. 1030 “On Approval of Forms of primary Medical Documentation of healthcare institutions” and the Medical record of a patient receiving medical care in inpatient conditions, in a Day hospital, approved by the Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated August 5, 2022 No. 530n “On Approval of Unified Forms of medical documentation used in medical organizations providing medical care in inpatient conditions, in the conditions of the day hospital and the procedures for their management”.
Results: based on the results of the study of two forms of “Cards”, the advantages of the new form have been established, which improve the quality of medical documentation and, as a result, taking into account the fact that the ECMP is carried out according to medical documentation, lead to a reduction in the risks of imposing financial sanctions on medical organizations during the relevant examinations. In particular, a number of shortcomings of the new form of the “Map” are indicated, requiring additional study and discussion with possible additions in the future.
Conclusions: the relevance of the examination of the quality of medical care, which, as a rule, is carried out according to the medical documentation of completed cases, is reflected. It is noted that the correct filling in of all the provided graphs and lines will minimize the number of defects in the registration of medical documentation, which in turn will reduce the financial sanctions imposed on medical organizations during the ECMP.
HISTORICAL OVERVIEW
The article analyzes materials from the State Archive of the Rostov Region about Zinaida Vissarionovna Ermolyeva, an outstanding Soviet microbiologist and epidemiologist, academician of the USSR Academy of Medical Sciences, creator of the first domestic drugpenicillin. Data are provided about her years of study at the Rostov Women's Medical Institute, and the nat the Faculty of Medicine of Don University. Archival materials are considered hat testify to the first stages of her career as a teacher and scientist at the Department of Microbiology of Don University.
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)