For the 80th anniversary of Victory in the Great Patriotic War
Objective: to provide a brief overview of the contribution of the Rostov-on-Don Antiplague Research Institute staff to ensuring sanitary and epidemiological well-being during the Great Patriotic War (WWII) in the south of the USSR. Materials and methods: analysis of archival materials and literary sources from the databases of electronic libraries E-library, CyberLeninka, etc. Results: the scientific and practical activities of the Rostov-on-Don Antiplague Institute during the WWII, carried out in cooperation with various organizations and structures of the country, are described. Particular attention is paid to information about the employees who contributed both to the work of the institute and to the common Victory. Conclusion: clear implementation of the system of preventive and anti-epidemic measures made it possible to avoid mass epidemics of infectious diseases during the war years. The experience accumulated during the WWII ensured that Soviet science reached the forefront in the post-war period. The "Scientific Regiment" of the Rostov-on-Don Antiplague Institute allows us to perpetuate the memory of scientists who worked and fought during the Great Patriotic War.
The article presents information about the activities of the Federal Budgetary Scientific Institution "Rostov Research Institute of Microbiology and Parasitology" of Rospotrebnadzor during the Great Patriotic War. The authors have combined materials about the work of the Institute in the pre-war, war and post-war years. The article is dedicated to people who managed to show all their best qualities in incredibly difficult conditions, unite and contribute to the Victory over the hated enemy. In the conditions of a shortage of personnel and medical equipment, the Institute's employees restored the activities of bacteriological laboratories and Pasteur stations, organized work to combat outbreaks of typhoid and typhus, cholera, eliminated the sanitary consequences of the war, continued the development of effective immunobiological drugs (vaccines, toxoids, serums), which made it possible to prevent the emergence and spread of infectious diseases, both at the front and in the rear.
3.1.4. OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
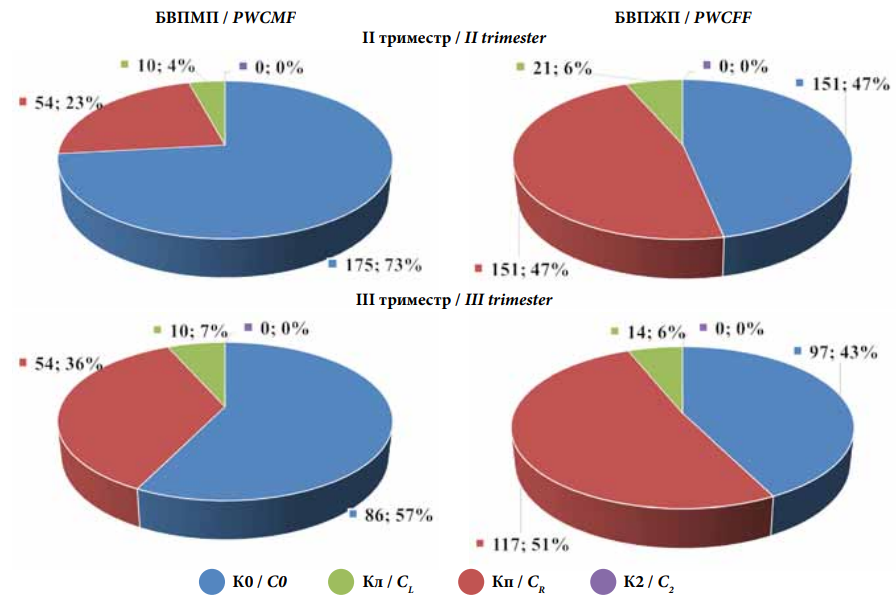
Objective: to study the features of contractile activity of the right and left sides of the uterus in patients with isthmiccervical insufficiency and uncomplicated pregnancy and to assess the nature of the gestational processes and labor outcomes depending on the sex of the fetus. Materials and Methods: a total of 146 patients with the functional form of isthmic-cervical insufficiency and 138 with uncomplicated pregnancy were examined. To study the nature of uterine activity of the right and left sides of the uterus, mechanohysterography was performed in the II and III trimesters of pregnancy. Results: in isthmic-cervical insufficiency in pregnant women with male fetuses with a higher incidence of preterm labor, bilateral uterine contractions predominated, whereas in uncomplicated pregnancy (dominated in pregnant women with female fetuses), unilateral (mainly right-sided) uterine contractions were detected. Conclusion: isthmic-cervical insufficiency is characterized by the predominance of functional symmetry in the myometrium, predominant in the case of the male fetus and leading to an increase in intraamniotic pressure and to dynamics from the length of the cervix, whereas physiological pregnancy is characterized by functional asymmetry, causing the preservation of the lower segment and the length of the cervix and more pronounced when bearing female fetuses.
Objective: determine the clinical and anamnestic risk factors leading to the formation of an incompetent uterine scar in patients after one previous cesarean section. Materials and methods: 102 histories of patients with a uterine scar after one cesarean section, 102 newborn charts, results of pathomorphological studies of the placentas for 2019–2020. All patients were divided into 3 groups: Group 1 (control) — 35 women with a uterine scar who gave birth vaginally; Group 2 (main group A) — 35 patients with established scar incompetence after one CS before delivery; Group 3 (main group B) — 32 patients with an unsuccessful attempt at vaginal delivery and intraoperatively established uterine scar incompetence after one CS. Results: It was established that an untenable scar on the uterus is associated with intrauterine interventions on the pelvic organs (p1.2=0.031, OR1.2=2.864; 95%CI=1.086–7.552), which were statistically significantly more common in group 2 compared with group 1. Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in the anamnesis were statistically significantly more common in group 2 compared with group 1 (p1.2=0.012, OR1.2=3.778; 95%CI=1.308–10.913). In group 3 with an unsuccessful attempt at vaginal delivery, genital endometriosis was statistically significantly more common compared with study groups 1 and 2 (p1.3=0.000001; p2.3=0.00003) (OR1.3=10.333. 95%CI=2.996–35.635; OR2.3=22,000; 95%DEE=4,547–106–437). In group 3, inflammatory changes in the placenta were more often noted. The emergency nature of CS and the intergenetic interval of less than 2 years and 9 months were mainly in patients with uterine scar failure. One of the most frequent indications in emergency COP was a disproportion between the size of the mother's pelvis and the fetal head, which was noted in group 1 statistically significantly more often than in groups 2 and 3 of the study (p1.2=0.0004; p1.3=0.0003) (OR1.2=10.074; 95%CI=2.595-39,112), (OR1.3=8,982; 95%CI = 2,311-34,911). Complications in the postoperative period were statistically significantly more common in groups with uterine scar failure. Conclusion: the main clinical and anamnestic risk factors leading to the formation of an incompetent scar were: intrauterine interventions, genital endometriosis, emergency nature of the operation, pelvic-cephalic disproportion, short intergenetic interval.
Objective: to investigate the effects of angiotensinogen on the endometrium in missed abortion. Materials and methods: a prospective cohort that included 212 women, 160 with missed abortion and 52 with progressing pregnancies at 6–12 weeks. In all participants, the average serum concentration of angiotensinogen was measured. Additionally, a morphological examination of the endometrium was performed in patients with missed abortion. Results: women with missed abortion had significantly lower angiotensinogen levels compared to those with progressing pregnancies. Based on the results of a nonparametric analysis, there was a direct correlation between low angiotensinogen levels and spiral artery thrombosis in missed abortion patients at 11–12 weeks (r=0,37, p<0,01). Conclusion: these findings suggest that a decrease in angiotensinogen levels is associated with impaired angiogenesis in the endometrium and can lead to spiral artery thrombosis during on the endometrium in missed abortion.
PSYCHIATRY AND NARCOLOGY
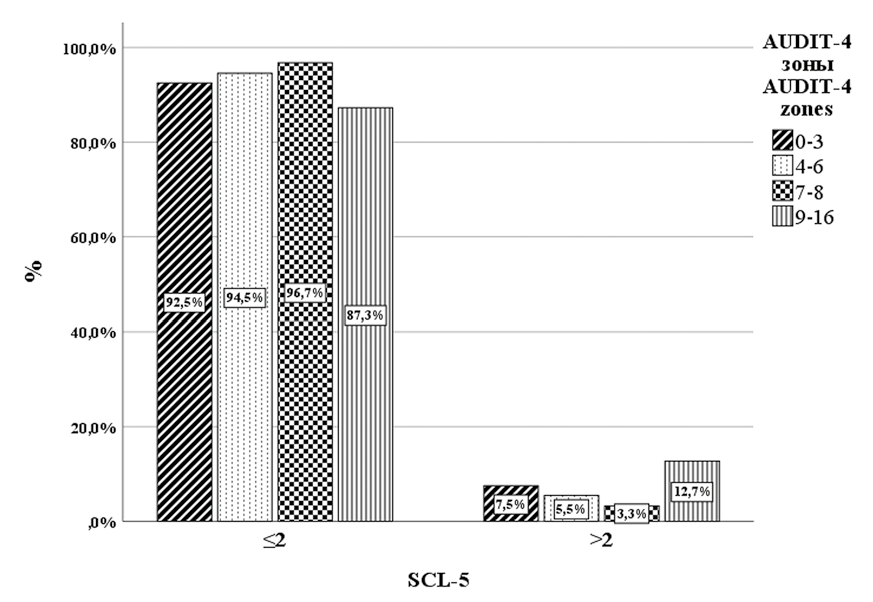
Objective: to study, using the SCL-5 questionnaire, the prevalence of mental distress in relation to alcohol consumption, socio-demographic and some clinical characteristics among somatic patients hospitalized in a clinical hospital. Materials and methods: the material was collected in 2016–2017 in V. P. Demikhov City Clinical Hospital of Moscow. 3009 patients were included in the study. Basic socio-demographic data were collected. Alcohol consumption was assessed using AUDIT-4, and the state of mental distress was assessed using SCL-5. Results: the number of women with more than two SCL- 5 points exceeded the number of men. Divorcees and widows were in mental distress more often. The distribution of the number of patients with distress according to the AUDIT-4 test zones had a “J”-shape. The groups “Therapeutic profile” and “Cardiologic profile” were the most prone for distress. Conclusion: early recognition and correction of mental distress in individuals with harmful alcohol use in primary care may improve patient compliance and treatment outcomes. The SCL-5 questionnaire has been shown to be a concise and convenient tool for diagnosing mental distress.
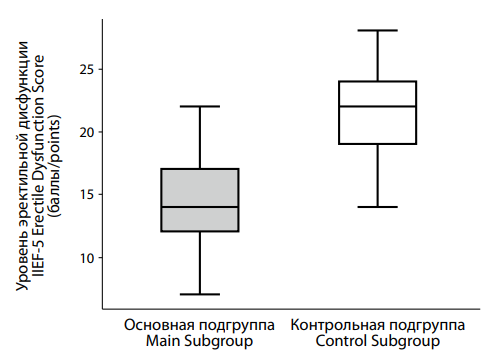
Objective: to study the clinical features of depression in men with low testosterone levels. Materials and methods: the study included 140 males aged 18 to 65 years diagnosed with recurrent depressive disorder (F33) and a depressive episode (F32) according to ICD-10. The main group consisted of men with depression comorbid with testosterone deficiency (n = 90). The control group included men with depression and normal testosterone levels (n = 50). Results: symptoms of depression in men with testosterone deficiency were less severe and led to less functional disturbance. There were some clinical differences in symptoms and syndromes such as sexual function, sleep, irritability, alcohol consumption, severe and functionality, main syndrome etc. For the main group was more typical mono-episode with manifestation at a later age while for the control group recurrent episodes manifesting at an earlier age were more typical. Conclusions: depression in men with testosterone deficiency has a number of differences that must be taken into account when diagnosing and choosing treatment tactics.
Objective: to assess the effect of untreated psychosis duration on the likelihood of involuntary hospitalization among patients with a first psychotic episode. Materials and methods: a retrospective analysis of data from patients admitted to inpatient treatment between 2020 and 2023 was conducted. Data was collected on the duration from the onset of the psychotic episode until hospitalization, as well as the reasons and circumstances leading to hospitalization, with clinical, psychopathological, and psychometric assessments of the patient's condition. Results: patients whose first episode of psychosis went untreated for more than 3 months were more likely to be hospitalized involuntarily compared to those who received treatment within the first month after symptom onset. Conclusions: the presence of destructive and autoaggressive behaviors, as well as gross psychoproductive symptoms and a high level of psychopathization, along with patient refusal of treatment increased the risk of hospitalization without consent. These findings emphasize the importance of early diagnosis and treatment for psychotic disorders, particularly in the case of a first episode. Early intervention can help reduce the risk of involuntary hospitalization and improve long-term treatment outcomes.
3.1.18. INTERNAL DISEASES
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) rank as the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Obesity, which is related to metabolic risk factors for CVD, is a common problem globally and in Russia. However, the generally accepted criteria for obesity cannot fully reflect the risk of developing CVD. According to modern concepts, visceral obesity is a more sensitive marker of CVD. The use of epicardial adipose tissue thickness (EAT thickness) is proposed for the determination of visceral obesity. In this regard, the presented review examines studies aimed at determining the threshold values of EAT thickness for more accurate risk prediction of CVD development. Growing interest in the potential influence of epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) on cardiovascular risk has led to an in-depth study of its functions. Genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors may contribute to a shift toward dysfunctional EAT, characterized by a proinflammatory and profibrotic phenotype. Due to its close anatomical proximity to the coronary arteries, thicker and dysfunctional EAT actively contributes to the development and progression of coronary atherosclerosis. In addition to classical paracrine transmission, EAT can directly release mediators into the vasa vasorum of the coronary artery wall, a mechanism termed “vasocrine.” Similarly, the proinflammatory and profibrotic secretome that characterizes dysfunctional EAT can impair cardiac structure and function, thus contributing to the pathogenesis of a large number of cardiovascular diseases.
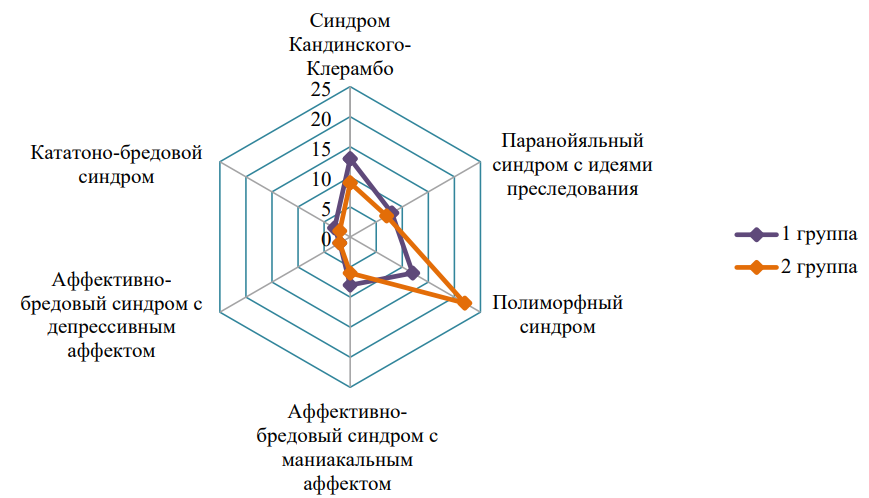
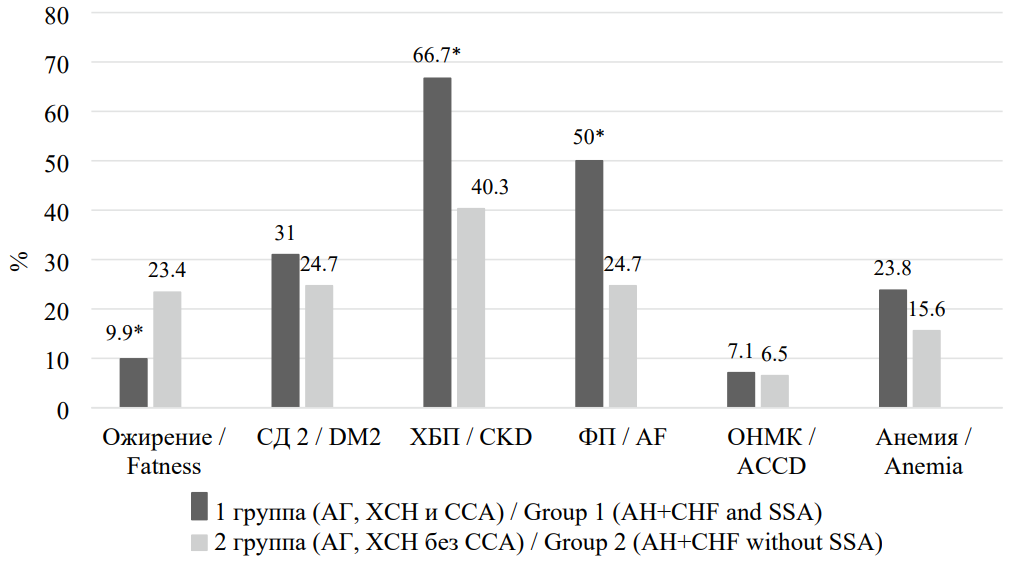
Objective: to evaluate the features of the structural and functional parameters of the heart in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) and senile asthenia syndrome (SSA). Materials and methods: the study involved 161 respondents with CHF on the background of arterial hypertension (AH) (82 women and 79 men) aged 80 to 91 years. Taking into account the presence of CSA, patients were divided into 2 groups: group 1 — patients with CHF and CSA (n = 84), group 2 — patients with CHF without CSA (n = 77). Screening and diagnosis of CSA were performed using the "Age is not a hindrance" questionnaire and a comprehensive geriatric assessment. To determine the structural and functional parameters of the heart, transthoracic echocardiography (EchoCG) and Doppler EchoCG studies were performed. Results: in patients with hypertension and CHF with the development of CSA, compared with patients with hypertension and CHF without CSA, statistically significantly higher values of indexed indicators of anterior-posterior LP size (ILP), LP volume (IOLP), left ventricular myocardial mass (LVMI) (p <0.05) were observed, as well as a higher percentage of the development of concentric LV remodeling (CRLH) and a smaller one — concentric LV hypertrophy (CRLH), which is associated with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events. Analysis of LV systolic function revealed significantly higher LV end systolic size index (ICSR), LV end diastolic size index (ICDR), LV end diastolic volume index (ICDO), LV end systolic volume index (ICSO), lower LV minute volume index (MO), this reflects a decrease in LV myocardial contractility. In addition, patients with CSA have a lower percentage of LV ejection fraction (EF): 44% versus 59.2% (p=0.002). Accordingly, among patients with CSA, a lower percentage of heart failure with preserved LV ejection fraction (LVEF) was detected (p = 0.028). There was a statistically significant decrease in DT, IVRT, and e' indices, as well as an increase in the E/e' ratio, which indicates a more pronounced progression of LV diastolic dysfunction in "fragile" patients with hypertension and CHF. Conclusion: in the presence of CSA, patients with hypertension and CHF aged 80 years and older showed more significant changes in the structural and functional parameters of the heart, indicating a more pronounced violation of systolic and diastolic function.
3.1.21. PEDIATRICS
A clinical case of indirect hyperbilirubinemia in a child with diabetic fetopathy is presented. Diagnosis and comprehensive treatment treatment of children with this pathology is difficult due to the variety of causes that cause the development of indirect or direct hyperbilirubinemia or a combination of them. Jaundice in young children is a frequent clinical symptom in practical medicine, and in severe cases may be accompanied by a manifestation of neurotoxicity of indirect bilirubin, accompanied by some delay in diagnosis, cases of prolonged course, or be a harbinger of a serious underlying disease, leading to fatal outcomes. Therefore, a symptom of jaundice should not be perceived as a routine condition. Regardless of the level of hyperbilirubinemia, the appearance of jaundice in the first 24 hours of life, the high rate of hourly increase in serum bilirubin levels, combined with the severity of hemolysis, require urgent examination and treatment of in young children. The main importance for the diagnosis and prognosis of the disease in children with hyperbilirubinemia is the rapid increase in jaundice with visible staining of the palms and feet. This requires an urgent determination of the concentration of bilirubin in the blood serum. It should be noted that in most cases, non-invasive, transcutaneous determination of bilirubin levels by a bilirubinometer does not replace standard laboratory testing, but allows you to avoid unjustified collection of capillary or venous blood in newborns and not miss dangerous hyperbilirubinemia, especially with early discharge from the hospital.
INFECTIOUS DISEASES
While recurrent bacterial pneumonia is a recognized indicator of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), cases exist where a single episode of pneumonia in HIV-positive individuals can progress rapidly and prove fatal. This article details the case of a patient hospitalized in the intensive care unit for HIV infection and bilateral pneumonia of unknown origin. The report outlines the progression of the illness, analyzes relevant laboratory and diagnostic imaging results, describes the implemented treatment plan, and identifies contributing factors that led to a fatal outcome. Current Russian clinical guidelines define AIDS in individuals with HIV infection who present with at least one AIDS-defining illness. These illnesses encompass a range of opportunistic infections and malignancies, including esophageal candidiasis, chronic cryptosporidiosis with diarrhea of more than one month duration , extrahepatic cytomegalovirus infection in individuals older than one month; Pneumocystis pneumonia, Kaposi's sarcoma, Burkitt's lymphoma, along with other types of B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; additionally, both brain toxoplasmosis and pulmonary tuberculosis in individuals aged older than one month and 13 or older respectively, are classified as AIDS-defining conditions.While bacterial pneumonia is classified as an AIDS-defining illness only when it reoccurs within a 12-month period, there are instances where HIV-positive patients develop severe, life-threatening pneumonia without prior documented episodes.
3.2.2 EPIDEMIOLOGY
Currently, denture care is becoming an important aspect of maintaining health, which affects the quality of life, especially for the elderly. Proper dental care plays an important role in preventing a number of oral diseases that can have a negative impact on the general health of the population. Untimely or insufficient care of dentures can lead to the development or be an aggravating factor in the course of systemic diseases of the body. Oral infections can increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes mellitus, as well as respiratory infections. Thus, the care of prostheses is associated with the prevention of general somatic diseases. Dentures are important for the restoration of full-fledged life activity in the elderly population, and the peculiarities of individual oral hygiene and care for orthopedic structures are the basis for reducing the risk of developing odontogenic and general somatic diseases. The analysis of sanitary and epidemiological features allowed us to characterize information about the prevalence of the use of dentures, as well as to search for relevant recommendations for their care aimed at maintaining the patient's health.
3.2.7 ALLERGOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Objective: identification of immunological features of oligomenorrhea in adolescent girls with excess weight. Materials and methods: the object of the study were 80 adolescent girls with excess weight and oligomenorrhea, who made up group 1, group 2 included 64 patients with obesity without cycle disorders. The control group — 25 healthy patients. Determination of the content of leptin, sR-leptin, IL-6, TNF-α, sTNF-αR1 was carried out by the method of solid-phase enzyme immunoassay (BenderMedSystems). Expression of TLR -2, TLR-4 was analyzed by flow cytometry (HyCultbiotechnology). Analysis of nucleotide polymorphism of the TLR-4 Asp299Gly gene was performed by PCR using the standard kit of the State Research Institute of Genetics (Russia). Descriptive statistics were performed using the Mann-Whitney criterion, with an error of the first kind p <0.05. To study the frequency of allele and genotype polymorphism by a binary feature, the χ2 criterion was used. Results: chronic inflammation is associated with metabolic disorders, dysregulation of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Oligomenorrhea in overweight patients is associated with an increase in the production of proinflammatory cytokines, the presence of mutations in the TLR-4 gene. Conclusions: the established changes potentiate ovarian dysfunction and the development of oligomenorrhea.
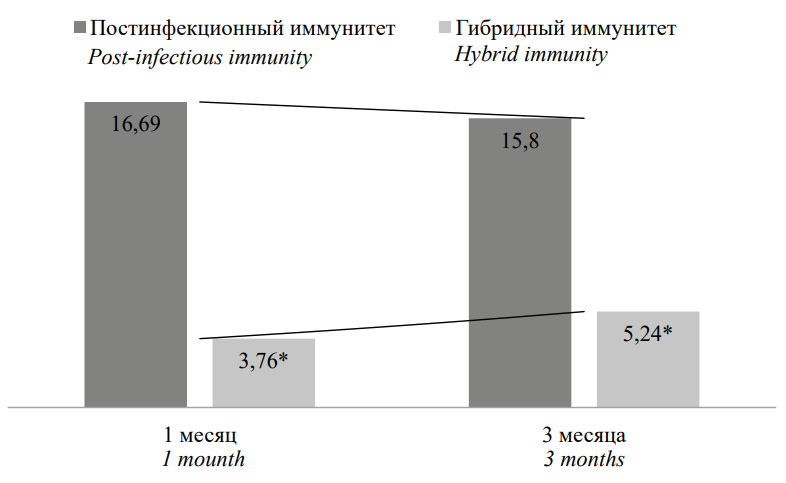
Objective: to assess the dynamics of changes in the levels of specific antibodies in individuals with a history of COVID-19 and those vaccinated with synthetic peptides of SARS-CoV-2. Materials and methods: 40 people who had COVID-19 and immunized with synthetic SARS-CoV-2 peptides were examined. Methods: ELISA diagnostics of specific antibodies to the S and N protein of SARS-CoV-2 and statistical. Results: with COVID-19 in the post-infectious period, the production of S-protein-specific IgG is observed throughout the year from the moment of recovery. Vaccination of recovered individuals with peptide antigens leads to increased synthesis of IgG not only to the S-protein, but also to the N protein of the coronavirus, with a stable tendency towards an increase in antibody content over 3 months of observation. Conclusions: humoral post-infectious immunity is characterized by the predominant production of IgG to the S-protein of SARS-CoV-2, which persist for a year from the moment of recovery, while hybrid immunity, along with the production of antibodies to the S-protein, promotes the predominant synthesis of Ig G to the N protein SARA -CoV-2.
Objective: to study and evaluate the state of adaptive immune response in patients with various coronary indices. Materials and methods: 62 male respondents of comparable age and risk factors for atherosclerosis participated in the study. Of these, 20 people with coronary atherosclerosis were in the moderate–risk group (group 1), 20 people with coronary atherosclerosis were in the high–risk group (group 2), and 22 people were in the control group. The assessment of coronary calcium and the calculation of the Agatston index were carried out using the software application for calculating coronary calcium Smart Score. The following CD3+, CD3+CD4+, and CD3+CD8+ populations were phenotyped with the calculation of the immunoregulatory index. B-lymphocytes (CD19+) were examined using flow cytofluorometry using appropriate monoclonal antibodies. Quantitative determination of the level of Ig A, M, G was carried out by radial immunodiffusion in gel using sets of monospecific antisera, expressed in g/L. Statistical analysis of the results of the study was carried out using the Statistica 12.0 program (StatSoft, USA). Results: in patients with coronary artery calcification, changes were detected in both the cellular and humoral components of adaptive immunity. Conclusion: these changes indicate the activation of the cytotoxic potential of CD8+ lymphocytes and the functional activity of B cells, which is the basis for further studies of the immune response in patients with coronary calcification, followed by the development of a universal screening tool.
SURGERY
Objective: to analyze the accumulated experience of the Rostov surgical school in providing care to patients with complicated portal hypertension, to discuss and present the author's view on the facts presented. Materials and methods: the surgical clinic of Rostov State Medical University has experience in treating more than 500 patients with cirrhosis of the liver since 1993. The stages of mastering surgical interventions began with the work of N.A. Bogoraz, who moved from the University of Warsaw to Rostov-on-Don. By 2007, 79 operations of proximal splenorenal (splenotesticular) venous bypass surgery (group I) were performed, from 2007 to 2024 315 operations of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic bypass surgery (group II). Results: analysis of intra- and postoperative complications revealed that intra-abdominal bleeding was registered in 5,06% in group I versus 0.31% in group II; varicose esophageal and gastric bleeding in the first 24 hours after surgery in 2,53% versus the absence of such a complication in group II, anemia after surgery requiring hemotransfusion in 34.17% against 0%, the development of hepatorenal syndrome in 7,59%, which led to death in group I versus 2,53% in group II. Conclusions: the Rostov Surgical School, which is one of the five centers in the Russian Federation that widely use TIPS/TIPS surgery in their arsenal, makes a definite contribution to improving the technique. But the issue of providing high-tech medical care to patients with cirrhosis of the liver remains open in its knowledge and development.
ISSN 2618-7876 (Online)