Scroll to:
Therapeutic-resort rehabilitation of children with gallbladder pathology living in ecologically unfavorable territories of the Krasnodar Region
https://doi.org/10.21886/2219-8075-2021-12-3-55-61
Abstract
Objective: To study the eff ectiveness of medical and preventive schemes of spa rehabilitation of children with biliary tract diseases living in ecologically unfavorable areas of the Krasnodar region.
Materials and Methods: The study was conducted among children aged 7 to 14 years old burdened with gallbladder pathology (dysfunctional disorders of the biliary tract (DRBT)). In 2017-2020, the eff ectiveness of the therapeutic-resort stage of rehabilitation was studied in 127 children. The children permanently resided in Krasnodar and were admitted to the therapeutic spa-resort center of mother and child “Diluch” in the resort city of Anapa. The authors selected 93 (73.2%) children with hypofunctional gallbladder disorder (GI) and 34 (26.8%) children with hyperfunctional GI disorder for spa treatment. The control group included children with the 1st group of health. The eff ectiveness of the applied methods of rehabilitation was evaluated based on laboratory and instrumental studies, as well as periodic dynamic medical examinations, which included the collection of complaints, physical examination, and palpation of the abdominal cavity.
Results: Therapeutic spa-rehabilitation of children with DRBT included balneotherapy, physiotherapy, and aerophytotherapy without the use of pharmacological drugs. At the same time, there was an improvement in the condition of both children with DRBT of the hypertensive type (94.1%) and among the subjects with DRBT of the hypotonic type (90.1). There were no cases of the condition worsening in the observed children with DRBT that permanently resided in unfavorable conditions of the Krasnodar Region.
Conclusions: Based on the obtained results, it can be suggested that diff erentiated comprehensive rehabilitation in the conditions of the balneological complex of the resort city of Anapa performed aft er the main treatment of gastrointestinal pathology is feasible for children and adolescents experiencing adverse environmental impacts at a permanent place of residence in the Krasnodar region.
For citations:
Nazaretyan V.G., Shashel V.A., Naumenko G.V., Borovleva L.I. Therapeutic-resort rehabilitation of children with gallbladder pathology living in ecologically unfavorable territories of the Krasnodar Region. Medical Herald of the South of Russia. 2021;12(3):55-61. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.21886/2219-8075-2021-12-3-55-61
Introduction
Spa resort rehabilitation of children with dysfunctional disorders of the biliary tract (DDBT) is highly efficient and widely used in the treatment of gastrointestinal pathology after inpatient and outpatient therapy [1][2]. Recreation at a balneological resort involves a wide range of rehabilitation methods like natural therapeutic factors (climate, mineral water, drug therapy) and instrumental physiotherapy [1][4]. A complete differential program of rehabilitation for patients with DDBT included all methods available at the therapeutic mother-and-child spa resort center "DiLUCH" in the resort city of Anapa [1]. The study was based on materials of previous observations and publications on the issue of spa resort rehabilitation of children with DDBT.
The study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the programs of spa rehabilitation of children with DDBT living in ecologically unfavorable areas of the Krasnodar Region.
Materials and Methods
The study included 127 children aged 7 to 14 years old with DDBT. In 2017–2020, the authors studied the efficiency of spa resort rehabilitation in the facilities of the therapeutic mother-and-child spa resort center "DiLUCH" in the resort city of Anapa. The children included in the study permanently resided in Krasnodar. All children underwent a preliminary complex examination at a diagnostic center for children, local polyclinics for children, or specialized Krasnodar regional clinical hospital for children. The minimum volume of examination included complete blood count and biochemical blood assay, clinical urine analysis, coprogram stool test, abdominal ultrasonography. The mean age of children was 11.2 ± 3.1 years old. All children had remission during the study. The study was conducted according to the international good clinical practice standards.
The spa resort rehabilitation program lasted 21 days. A total of 93 children (73.2%) with hypofunction disorder of the biliary tract and 34 children (26.85) with hyperfunction disorder of the biliary tract were included in the study. The control group included 118 children with the first group of health that came for resort vacations to the recreation center from Krasnodar.
The effectiveness of complex rehabilitation was scored by the scale used in the previous studies. The dynamics of the studied parameters corresponded to a certain score that was introduced in the formula of the Treatment Efficiency Index (TEI). After the calculation, the authors obtained the coefficient that was used to evaluate the quality of the spa resort treatment. The statistical analysis of the obtained data was performed in the software packages Excel Microsoft Office 2007 and STATISTICA 6.0.
Results
A complex differential program of rehabilitation for children in the spa resort facilities included moderate climate, therapeutic exercises, diet (No. 5, reduction of plant oils in meals), heliotherapy and thalassotherapy, mineral water (depending on the DDBT type), iodine-bromine baths, gall bladder cleanse procedures with mineral water proposed by Demianov (according to the classic scheme), galvanization with sulfide mud, ultraviolet therapy, aerophytotherapy, massage, and acupuncture. It should be mentioned that pharmacotherapy was not used. The control group received standard nutrition, physical activities, physio and balneo procedures according to the schemes of recreation recommended for healthy children [4].
The efficiency of the applied methods of rehabilitation was evaluated by the obtained laboratory and instrumental data, as well as periodic dynamic medical examinations that included the collection of anamnesis, complaints, physical examination, and abdominal palpation (Figures 1, 2).

Figure 1. Complaints in children with DDBT living in environmentally unfavorable areas before and after rehabilitation (hypofunction).
Based on the data presented in Figures 1 and 2, a decrease in the pain syndrome was observed in children, as well as manifestations of dyspepsia (nausea and burp), and an improvement of intestinal function. After the treatment, the number of complaints of constipation decreased among children with hypo and hyperfunction of the bladder. Such symptoms as heartburn and vomit completely resolved.

Figure 2. Complaints in children with DDBT living in environmentally unfavorable areas before and after rehabilitation (hyperfunction).
The efficiency of spa resort treatment was also confirmed by the analysis of laboratory parameters (Table 1, 2). The results revealed a positive dynamic by the end of the rehabilitation period. Thus, there were no residual pesticide traces revealed. In children with hypofunction of the bladder, the levels of hemoglobin improved, the content of protein normalized, and the levels of ALaT and ASaT significantly decreased. Besides, there were positive changes in children with hyperfunction of the bladder. It should be mentioned that in both groups, the levels of alkaline phosphatase significantly decreased, which indicated the normalization of liver function after the improvement of bile evacuation. After the resort recreational treatment, total and direct bilirubin levels normalized in both groups.
Laboratory parameters indicate the efficiency of the applied methods of rehabilitation. The evaluation of the effectiveness was also verified with methods of mathematical analysis.
Table 1
Laboratory parameters in children with DDBT (hypofunction) residing in ecologically unfavorable territories before and after rehabilitation
|
Laboratory parameters |
Control group |
Hypofunction |
|
|
Start of rehabilitation |
Completion of rehabilitation |
||
|
n = 118 |
n = 93 |
n = 93 |
|
|
Hemoglobin, g/l |
128±7.34 |
107.2±4.12 |
129.9±6.31 |
|
White blood cells, ×109/l |
7.1±0.60 |
4.7±0.30 |
7.2±0.59 |
|
Total protein, g/l |
78.0±2.99 |
64±1.30 |
75.3±3.32 |
|
Total bilirubin, µmol/l |
18.1±0.99 |
31.9±2.13 |
14.8±1.02 |
|
Direct bilirubin, µmol/l |
0.68±0.03 |
28.6±1.88 |
0.71±0.04 |
|
Amylase, units/l |
52.0±2.03 |
46.3±2.72 |
51.2±1.99 |
|
AsAT, units/l |
20.8±1.80 |
46.1±2.13 |
15.1±0.75 |
|
AlAT, units/l |
35.4±3.10 |
56.2±3.41 |
34.8±2.12 |
|
ALP, units/l |
150.0±9.12 |
540±41.2 |
168.8±10.53 |
|
DDT, mg/l |
– |
0.18±0.003 |
– |
|
α-HCG |
– |
0.09±0.004 |
– |
|
γ-HCG |
– |
0.06±0.001 |
– |
Table 2
Dynamics of laboratory parameters in children with DDBT (hyperfunction) residing in ecologically unfavorable territories before and after rehabilitation
|
Laboratory parameters |
Control group |
Hyperfunction |
|
|
Start of rehabilitation |
Completion of rehabilitation |
||
|
n=118 |
n=34 |
n=34 |
|
|
Hemoglobin, g/l |
127.5±7.34 |
105.5±6.73 |
136.6±5.99 |
|
White blood cells, ×109/l |
7.1±0.60 |
4.9±0.32 |
7.1±0.54 |
|
Total protein, g/l |
78.0±2.99 |
58.9±2.75 |
77.0±3.13 |
|
Total bilirubin, µmol/l |
18.1±0.99 |
32.3±2.71 |
17.2±0.9 |
|
Direct bilirubin, µmol/l |
0.68±0.03 |
28.5±1.90 |
0.64±0.05 |
|
Amylase, units/l |
52.0±2.03 |
49.7±2.13 |
49.9±2.04 |
|
AsAT, units/l |
20.8±1.80 |
48.4±2.31 |
13.2±0.98 |
|
AlAT, units/l |
35.4±3.10 |
58.9±2.77 |
34.2±1.97 |
|
ALP, units/l |
150.0±9.12 |
493.3±39.40 |
156.8±10.83 |
|
DDT, mg/l |
– |
0.19±0.004 |
– |
|
α-HCG |
– |
0.08±0.003 |
– |
|
γ-HCG |
– |
0.06±0.002 |
– |
Discussion
The evaluation of the effectiveness of rehabilitation was made by the scale of patients’ condition in dynamic. The criteria for evaluation were laboratory, instrumental, and functional parameters that were registered in dynamics through the period of recreation at the resort (Table 1, 2). The obtained scores were summed and used in the formula for the calculation of the TEI [4]:
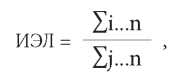
ИЭЛ – TEI
i – score of the clinical parameter condition before rehabilitation;
j – score of the clinical parameter condition after rehabilitation (Table 3);
n – number of parameters.
Table 3
Criteria for the effectiveness of rehabilitation of children with DDBT score
|
Parameters |
Score |
|||
|
Score 1 |
Score 2 |
Score 3 |
Score 4 |
|
|
White blood cells, ×109/l |
< 7 |
8–9 |
10–12 |
> 12 |
|
Hemoglobin, g/l |
> 120 |
120–110 |
110–100 |
< 100 |
|
Total protein, g/l |
> 70 |
69–61 |
60–50 |
< 50 |
|
Total bilirubin, µmol/l |
5–20 |
21–30 |
31–40 |
> 40 |
|
Direct bilirubin, µmol/l |
0–0.68 |
0.69–10 |
11–20 |
> 20 |
|
Amylase, units/l |
25–130 |
131–140 |
141–150 |
> 150 |
|
AsAT, units/l |
8–20 |
21–30 |
31–40 |
> 40 |
|
AlAT, units/l |
13–40 |
41–50 |
51–60 |
> 60 |
|
ALP, units/l |
Girls: 100–320 Boys: 100–390 |
Girls: 321–400 Boys: 391–450 |
Girls: 401–500 Boys: 451–550 |
Girls: >500 Boys: > 550 |
Results
TEI = 1.75 – significant improvement,
TEI = 1.30–1.74 – improvement,
TEI = 1.10–1.29 – insignificant improvement,
TEI = 1.09–1.0 – without worsening,
TEI < 1.0 – worsening.
Score 1. The condition is satisfactory. A child feels well. There are no complaints of pain, dyspeptic, and asthenovegetative syndromes. Palpation in the pyloroduodenal region is painless. Gastroscopy results are within the norm. Liver, gallbladder, and pancreas ultrasonography is within the norm. There are no gallbladder kinks. The vascular pattern is normal; the gallbladder lumen is homogenous. There is no suspension in the gallbladder. The size of the common bile duct is <6 mm.
Score 2. The condition is satisfactory. There is positive dynamic in the well-being of the child. The child does not have complaints. Palpation in the pyloroduodenal region is painless. No hyperemia by the results of gastroscopy. The gastric outlet is patent. The volume of gastric mucus is decreased. There are minor motor-evacuator deviations from the norm. Abdominal ultrasonography reveals a functional kink in the gallbladder neck. The contour is even; the walls are not altered. The gallbladder lumen is non-homogeneous. Single suspended particles are observed. The size of the common bile duct is <6 mm.
Score 3. The condition is of moderate severity. There is no positive dynamic. Palpation in the pyloroduodenal region is moderately painful. Gastroscopy shows hyperemia of the gastric mucosa and duodenum. Motor-evacuator function is impaired in the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. In the postbulbar section, a bile passage is observed. The echostructure and echogenicity of the liver and pancreas are altered. There are gallbladder neck kinks. The vascular pattern is normal. Single suspended particles are observed in the gallbladder lumen. The size of the common bile duct is ≥6 mm.
Score 4. The condition is of moderate severity. A child complains of abdominal pain, dyspeptic, and asthenovegetative syndromes. Palpation in the pyloroduodenal region and right upper quadrant is painful. Gastroscopy shows altered gastric mucosa and duodenum with hyperemia. There are significant motor-evacuator impairments in the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The bile passage is visualized well. The echostructure and echogenicity of the liver and pancreas are altered. There are gallbladder neck kinks. An increase in the right liver lobe is registered. There are single thickened vascular walls. The gallbladder contains ointment-like bile. The size of the common bile duct is >6 mm.
The condition of children with DDBT in remission improved significantly after balneotherapy and physiotherapy, as well as other methods of rehabilitation for children with gastrointestinal pathology, at the mother-and-child spa resort center “DiLUCH” (Figure 3): 61.3% of children with DDBT of hypotonic type completed a course of balneotherapy with the improvement of their condition and 14.0% completed a course of therapy with significant improvement. At the same time, an insignificant improvement was observed in 15.1% of cases. Similar dynamics of patients’ condition was observed in patients with DDBT of hypertonic type: significant improvement of the condition in 14.7% of patients, improvement – in 73.5% of patients, insignificant improvement – in 2 children (5.9%), and no changes were observed in 2 children (5.9%). The obtained results are presented in Figure 3.

Figure 3. The effectiveness of rehabilitation of children with DDBT.
Conclusion
A complex differentiated program of rehabilitation of children with DDBT (depending on the type of functional disorder) that permanently reside in the unfavorable conditions of the Krasnodar Region was shown to be an efficient method of additional treatment after inpatient and outpatient therapy. A special diet, climate, physical activity, balneotherapy, mud therapy, massage, physiotherapy, acupuncture, and aerophytotherapy provided the basis for a highly efficient rehabilitation for children with DDBT at the facilities of a spa resort balneological complex in Anapa.
References
1. Ivashkin V.T., Mayev I.V., Shulpekova Yu.O., Baranskaya Y.K., Okhlobystin A.V., et al. Diagnostics and treatment of biliary dyskinesia: clinical guidelines of the Russian gastroenterological Association. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2018;28(3):63-80. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.22416/1382-4376-2018-28-3-63-80
2. Andreyev D.N., Zaborovsky A.V., Trukhmanov A.S., Mayev I.V., Ivashkin V.T. Evaluation of the functional gastrointestinal diseases concept from standpoints of Rome IV (2016) diagnostic criteria (review). Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2017;27(1):4- 11. (In Russ.) DOI: 10.22416/1382-4376-2017-27-1-4-11
3. Polunina T.E. Аlgoritm diagnostiki i lecheniya disfunktsij biliarnogo trakta. Archive of Internal Medicine. 2015;1(21):27-32. (In Russ.). DOI: 10.20514/2226-6704-2015-0-1-27-32
4. Shashel V.A., Nazaretyan V.G., Naumenko G.V., Baloyan S.A. Comprehensive stage rehabilitation of children and adolescents with dysfunctional biliary tract disorders living in environmentally unfavourable territories of the Krasnodar Region. Detskaya i podrostkovaya reabilitaciya. 2020;1(2):58-64. (In Russ.). eLIBRARY ID: 44742734
5. Razumov A.N. Nauchno-prakticheskoe obespechenie realizacii strategii zdorov'esberezheniya naseleniya v ramkah vypolneniya Ukaza Prezidenta Rossii «O nacional'nyh celyah i strategicheskih zadachah razvitiya Rossijskoj Federacii na period do 2024 goda» // Materialy Vserossijskogo nauchnoprakticheskogo foruma «Zdravnica-2019». Maj 21-23, 2019; Alushta. (In Russ). Available at: https://rumed.ru/12390-2/Accessed April 30, 2021.
About the Authors
V. G. NazaretyanРоссия
Valerij G. Nazaretyan, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Professor, of the Department of Pediatrics №1
Krasnodar
V. A. Shashel
Россия
Victoria A. Shashel, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Professor, head of of Pediatrics №1
Krasnodar
G. V. Naumenko
Россия
Galina V. Naumenko, Cand. Sci. (Med.), assistant of the Department of Pediatrics 2
Krasnodar
L. I. Borovleva
Россия
Larisa I. Borovleva, student, headman of the SNO circle of the Department of Pediatrics №1
Krasnodar
Review
For citations:
Nazaretyan V.G., Shashel V.A., Naumenko G.V., Borovleva L.I. Therapeutic-resort rehabilitation of children with gallbladder pathology living in ecologically unfavorable territories of the Krasnodar Region. Medical Herald of the South of Russia. 2021;12(3):55-61. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.21886/2219-8075-2021-12-3-55-61
JATS XML







































